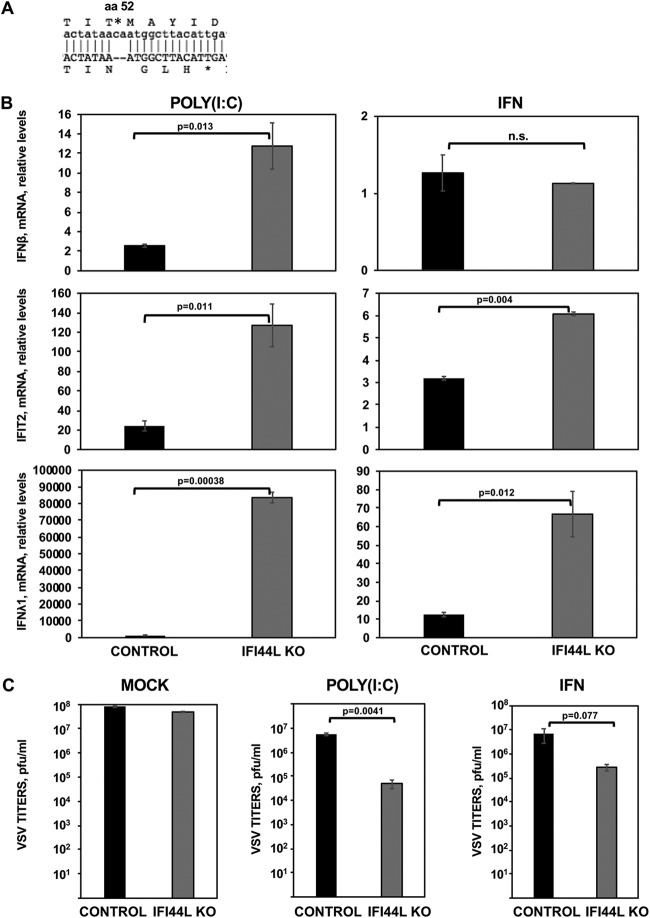
FIG 5.
IFI44L impairs antiviral responses. (A) Sequence alignment of HAP-1 control cells at the amino acid (aa) and nucleotide levels (top letters) and of HAP-1 IFI44L KO cells (bottom letters). The IFI44L KO cells encode a 2-nt frameshift deletion in the codon encoding amino acid 52, leading to a frameshift, and to the generation of a stop codon at codon 56. (B and C) Parental (CONTROL) and IFI44L KO HAP-1 cells were transfected with poly(I·C) or treated with 2,000 U/ml of IFN-α during 16 h. (B) Total cellular RNA was purified, and levels of IFN-β (top), IFIT2 (middle), and IFN-λ1 (bottom) mRNAs were evaluated by RT-qPCR and are represented as fold change values compared to values in mock-treated cells. Bars represent SDs of results determined using duplicate wells. Three different experiments were performed with similar results. P values determined by using a Student's t test are indicated for comparisons between WT and IFI44L KO HAP-1 cells. (C) Cells left mock treated (left), transfected with poly(I·C) (center), or treated with 2,000 U/ml of IFN-α (right) were infected with rVSV-GFP (MOI, 0.1). Virus production was analyzed at 24 hpi. Bars represent SDs of results determined using duplicate wells. Three different experiments were performed, with similar results. *, P < 0.05 (for comparisons between HAP-1 WT and IFI44L KO cells).