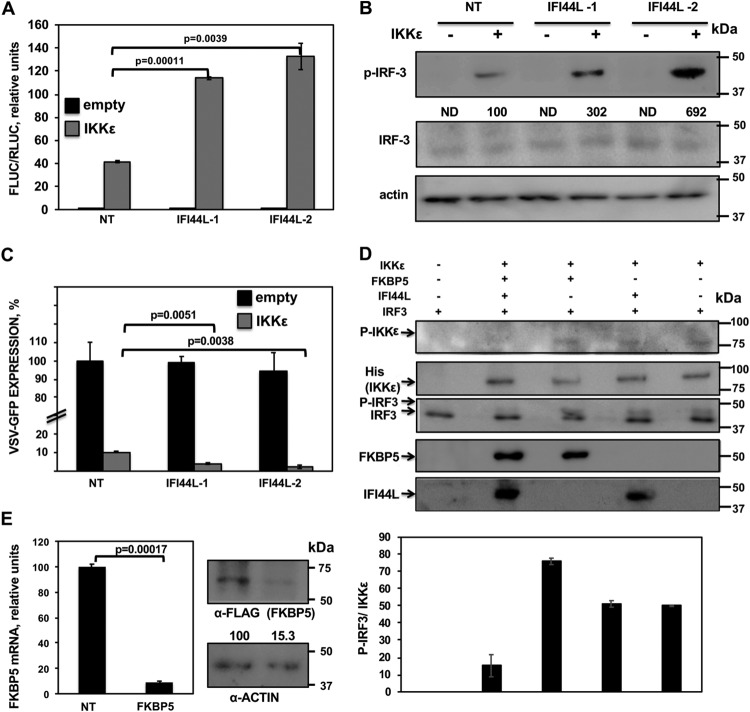
FIG 8.
IFI44L modulates IKKε kinase activity. (A and B) Human 293T cells were silenced for IFI44L, and, 36 h later, cells were cotransfected with a pCAGGS-His-IKKε plasmid together with a plasmid expressing Fluc under the control of an IFN-β promoter (pIFNβ-Fluc) and a plasmid constitutively expressing Rluc under the control of a simian virus 40 (SV40) promoter. (A) At 24 hpt, levels of Fluc were determined and normalized to the levels of Rluc. Data represent means and SDs of results from triplicate wells. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. P values determined by using a Student's t test are indicated. (B) Protein levels of p-IRF-3, total IRF-3, and actin (control) in extracts from cells treated as described for panel A were evaluated by Western blotting. Western blots were quantified by densitometry using ImageJ software (v1.46), and the amounts of p-IRF-3 were normalized to the amounts of total IRF-3 (numbers below the p-IRF-3 blot). Levels of pIRF-3 in cells silenced with the NT siRNA and transfected with the plasmid expressing IKKε were assigned a value of 100 for comparisons with pIRF-3 levels in IFI44L-silenced cells. ND, not detected. Molecular weight markers are indicated in the right (in kilodaltons). (C) Cell culture supernatants from cells treated as described for panel A were used to treat A549 cells for 24 h and infected with rVSV-GFP (MOI, 0.1). GFP expression was quantified in a microplate reader at 24 hpi. Data represent means and SDs of results from triplicate wells. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. P values determined by using a Student's t test are indicated. (D) Human 293T cells were silenced for IFI44 or FKBP5 and were transfected with plasmids expressing His-IKKε, IFI44L-HA, and FKBP5-FLAG. At 24 hpt, IKKε complexes were purified with an anti-His antibody and assayed in a kinase assay using recombinant human IRF-3 as the substrate. Levels of total and phosphorylated forms of IRF-3 were analyzed by Western blotting using specific antibodies. Levels of IKKε were determined using an anti-His-specific antibody and levels of phospho-IKKε were evaluated using an anti-p-IKKε antibody by Western blotting. Levels of IFI44L-HA and FKBP5-FLAG proteins were detected with anti-HA-specific and anti-FLAG-specific antibodies, respectively. Protein bands were quantified by densitometry using ImageJ software (v1.46), and levels of pIRF-3 were normalized to the levels of IKKε (bottom graphic). The results show error bars and means of results from two independent experiments. Molecular weight markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated on the right. (E) Human 293T cells were transfected with NT-specific or FKBP5-specific siRNAs for 36 h. (Left) Total RNAs were extracted and expression of FKBP5 mRNA was evaluated by RT-qPCR. Error bars represent the SDs of measurements in triplicate wells. The P value for comparisons between NT-transfected cells and FKBP5 siRNA-transfected cells performed using a Student’s t test is indicated. On the right, at 36 h after siRNA transfection, cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing FKBP5-FLAG for 24 h. Western blot analyses using an anti-FLAG-specific antibody (to detect FKBP5 expression) and anti-actin antibody (internal control) were performed. Protein expression levels in cells silenced with the NT siRNA were assigned a value of 100% for comparison with the level of expression in FKBP5-silenced cells (numbers below the anti-FLAG blot). FKBP5 expression was normalized to actin expression. Molecular weight markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated on the right. Three different experiments were performed with similar results.