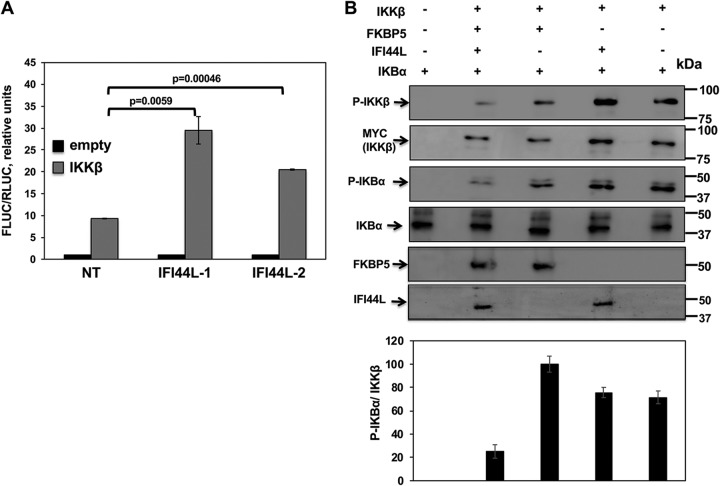
FIG 9.
IFI44L modulates IKKβ activity. Human 293T cells were transfected with two different siRNAs targeting IFI44L; 36 hpt, cells were cotransfected with pCAGGS-myc-IKKβ together with a plasmid expressing the Fluc under the control of an NF-κB-driven promoter (pNF-κB-Fluc) and a plasmid constitutively expressing Rluc under the control of the SV40 promoter. (A) At 24 hpt, levels of Fluc were determined and normalized to the levels of Rluc. Data represent means and SDs of results from triplicate wells. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. P values determined by using a Student's t test are indicated. (B) Human 293T cells were silenced for IFI44 or FKBP5 and were transfected with plasmids expressing myc-IKKβ, IFI44L-HA, and FKBP5-FLAG. At 24 hpt, IKKβ complexes were purified with an anti-myc antibody and were used in a kinase assay with recombinant human IκBα as the substrate. Levels of phosphorylated and total IκBα were analyzed by Western blotting using specific antibodies. Levels of IKKβ were also analyzed using an anti-myc-specific antibody and phospho-IKKβ. Levels of IFI44L-HA and FKBP5-FLAG proteins were detected with anti-HA-specific and anti-FLAG-specific antibodies, respectively. Protein bands were quantified by densitometry using ImageJ software (v1.46). Levels of p-IκBα were normalized to the levels of IKKβ (bottom graphic). The results show error bars and means of results from two independent experiments. Molecular weight markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated on the right.