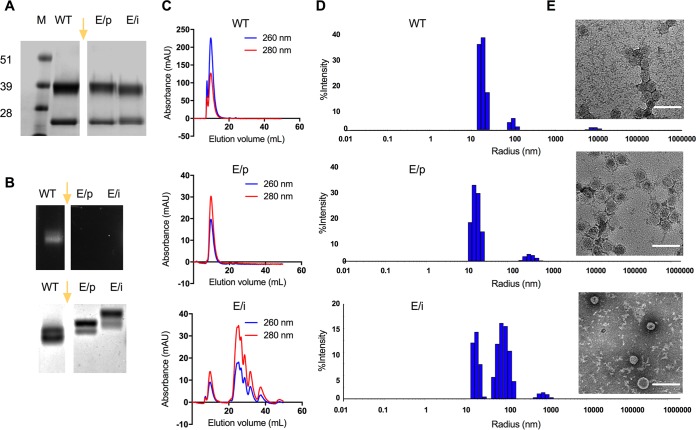
FIG 1.
Characterization of CPMV and eCPMV particles. (A) SDS gels following electrophoresis and staining with Coomassie brilliant blue. (B, top) GelRed nucleic acid gel under UV light; (bottom) the same gel following electrophoresis and staining with Coomassie brilliant blue. Lanes: M, SeeBlue Plus2 molecular weight marker; WT, wild-type CPMV; E/p, empty CPMV from plants (eCPMV/p); E/i, empty CPMV from insect cells (eCPMV/i). The gel images in panels A and B were spliced, as indicated by the gap and yellow arrow. The original gels included additional samples not discussed in this paper; therefore, these lanes were omitted from the figure. (C) Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) analysis of CPMV (top), eCPMV/p (middle), and eCPMV/i (bottom) particles. Blue, 260 nm; red, 280 nm; mAU, milli-absorbance units. (D and E) Sizes of wild-type CPMV (top), eCPMV/p (middle), and eCPMV/i (bottom) measured by dynamic light scattering (D) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (E). Bars, 100 nm.