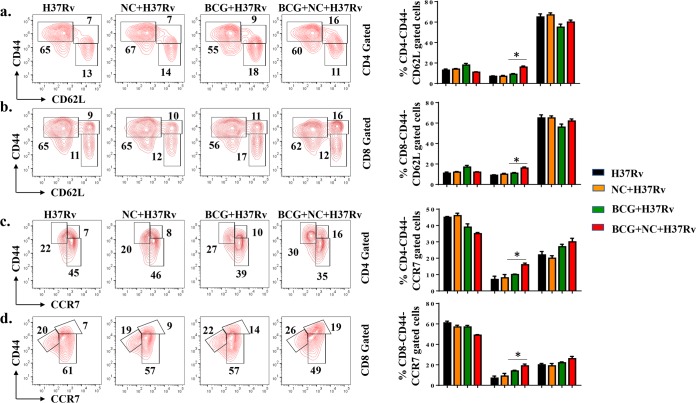
FIG 6.
Nanocurcumin enhances the TCM/TEM cell ratio in lungs of BCG-immunized mice. Mice were treated as described in the legend to Fig. 2a. At 75 days postinfection, lungs were harvested, and single-cell suspensions were made. Cells were cultured overnight with the M. tuberculosis lysate (CSA) and stained to assess antigen-specific immune responses. Cells were stained with anti-CD3, -CD4, -CD8, -CD44, -CD62L, and -CCR7 antibodies, followed by flow cytometry. Different memory subsets, including naive T cells (CD4+ CD44− CD62L−/CD4+ CD44− CCR7− or CD8+ CD44− CD62L−/CD8+ CD44− CCR7−), TCM cells (CD4+ CD44+ CD62L+/CD4+ CD44+ CCR7+ or CD8+ CD44+ CD62L+/CD8+ CD44+ CCR7+), and TEM cells (CD4+ CD44+ CD62L−/CD4+ CD44+ CCR7− or CD8+ CD44+ CD62L−/CD8+ CD44+ CCR7−), were analyzed by flow cytometry. (a) Contour plots and bar diagrams of different (CD62L-gated) CD4+ T memory subsets in lungs of different experimental groups. (b) Contour plots and bar diagrams of different (CD62L-gated) CD8+ T memory subsets in lungs of different experimental groups. (c) Contour plots and bar diagrams of different (CCR7-gated) CD4+ T memory subsets in spleens of different experimental groups. (d) Contour plots and bar diagrams of different (CCR7-gated) CD8+ T memory subsets in spleens of different experimental groups. All data are representative of results from 3 independent experiments with 5 mice from each experimental group at each time point. All values are represented as means ± SD. Statistical analyses were done by ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. * denotes a P value of ≤0.05. Experimental groups are (i) H37Rv, (ii) nanocurcumin (NC) plus H37Rv, (iii) BCG plus H37Rv, and (iv) BCG plus nanocurcumin and H37Rv.