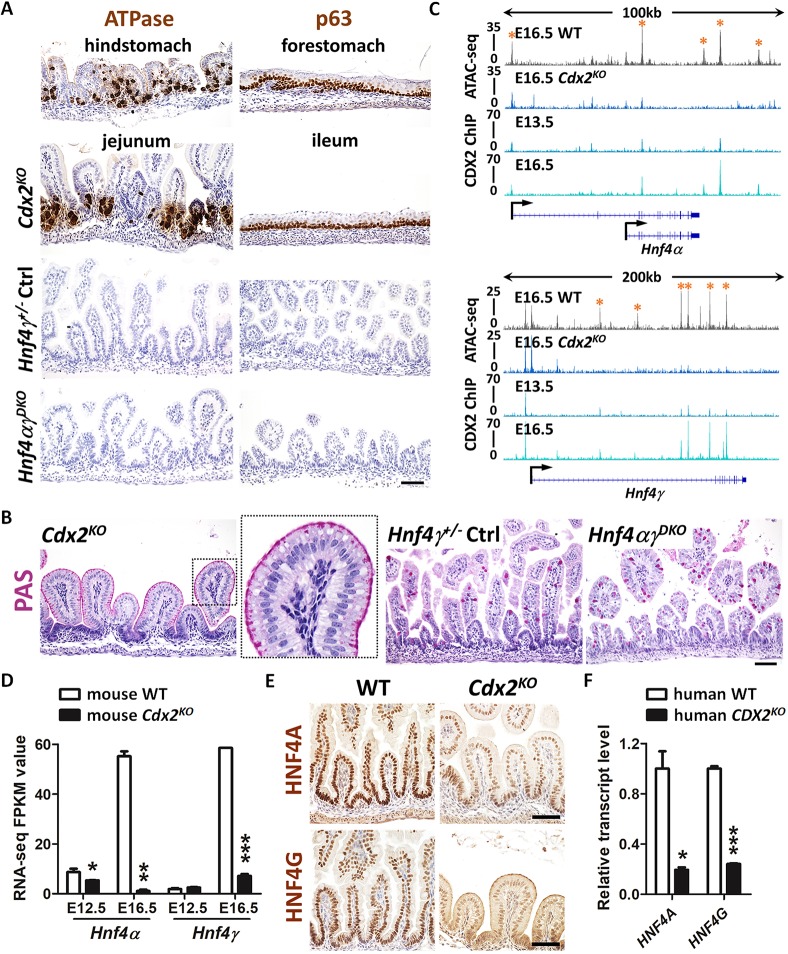
Fig. 2.
HNF4 is activated by CDX2 in the developing gut, but HNF4 is not required for intestinal specification. (A) Immunostaining of ATPase and p63 (representative of four biological replicates) in E18.5 control, Shh-Cre;Cdx2f/f (Cdx2KO) and Shh-Cre;Hnf4af/f;Hnf4gCrispr/Crispr (Hnf4αγDKO) embryos. The hindstomach marker ATPase is ectopically expressed in the Cdx2KO jejunum but not in the control and Hnf4αγDKO jejunum. The forestomach marker p63 is ectopically expressed in the Cdx2KO ileum (squamous mucosa) but not in the control and Hnf4αγDKO ileum. (B) PAS staining indicates that normal intestinal goblet cells are replaced with cells resembling gastric foveolar cells (PAS-positive cells at apical cell surface) in the Cdx2KO jejunum of E18.5 embryos, but not in the control or Hnf4αγDKO jejunum (representative of four biological replicates). (C) CDX2 binds to Hnf4a and Hnf4g loci at E13.5 and E16.5 (CDX2 ChIP, GSE115314, n=2 biological replicates; whole small intestine epithelium), and accessible chromatin is compromised at gene loci of Hnf4a and Hnf4g upon CDX2 loss (ATAC-seq, GSE115314, n=2 biological replicates; whole small intestine epithelium). Asterisks denote putative regulatory regions. (D) The transcript levels of Hnf4a and Hnf4g are significantly downregulated in the intestinal epithelial cells of the Shh-Cre;Cdx2KO. Data are presented as mean±s.e.m (RNA-seq, GSE115541, n=2 or 3 biological replicates; whole small intesitne epithelium). Statistical tests are embedded in DESeq2 at ***P<0.001, **P<0.01 and *P<0.05. (E) Immunostaining of HNF4A and HNF4G shows reduced protein levels of HNF4 paralogs in E18.5 Cdx2KO (representative of four biological replicates). (F) qRT-PCR shows reduced transcript levels of HNF4A and HNF4G in human intestinal organoids derived from CDX2CrisprKO human ESCs compared with organoids derived from control cells. Data are presented as mean±s.e.m. (n=3 biological replicates, Student's t-test, two-sided at P<0.001*** and P<0.05*). Scale bars: 50 μm in A,B,E.