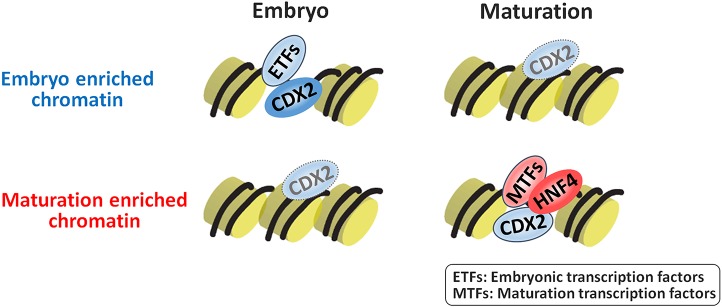
Fig. 7.
Potential model of how intestinal transcription factor networks shift as embryos mature to adults. Left: CDX2 functions in gut specification, and robustly binds to embryo-enriched accessible chromatin regions with other embryonic transcription factors. In the embryo, lower-level CDX2 binding might also occur at regions that will become accessible in the fetus. Right: As intestine matures to fetal stages, maturation-enriched regions become more accessible. A new transcription factor network, highlighted by HNF4, works together to stabilize enhancer chromatin and drive intestinal maturation.