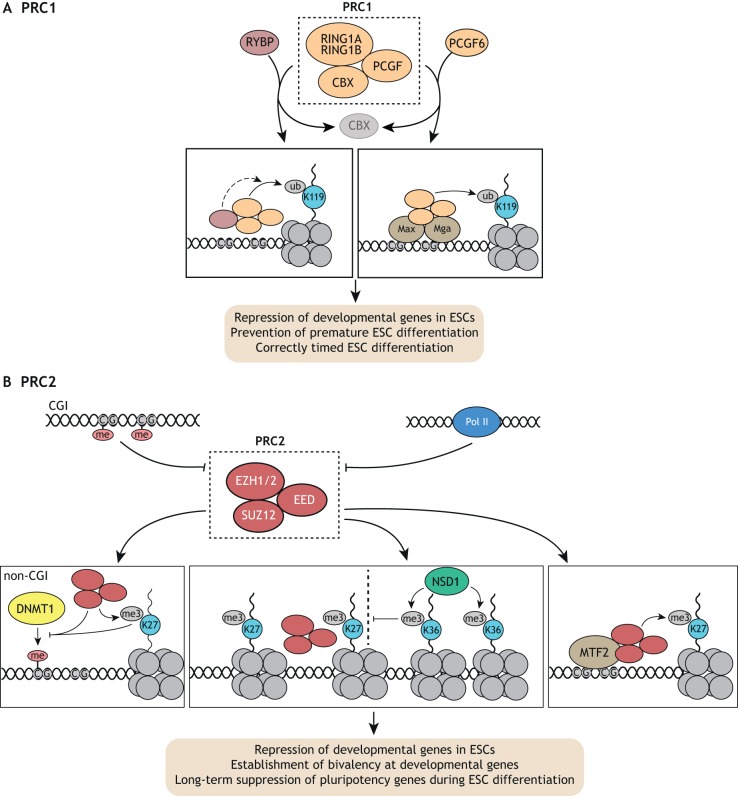
Fig. 3.
PRC1 and PRC2 functions in ESCs. (A) The PRC1 complex, consisting of core members RING1A/B, CBX and PCGF proteins, is responsible for ubiquitylation (ub) of H2AK119. Additional regulatory proteins such as RYBP can tune its ubiquitylation activity and PCGF6 can promote its recruitment by MAX/MGA. PRC1 is required for proper repression of developmental genes and premature differentiation in ESCs, and for correctly timed ESC differentiation. (B) The PRC2 complex, consisting of core members EZH1/2, EED and SUZ12, is responsible for trimethylation (me3) of H3K27. DNA methylation at CGIs and active Pol II oppose PRC2 recruitment, whereas MTF2 recruits PRC2 to unmethylated CG-rich regions. PRC2 activity in turn opposes DNA methylation by DNMT1 at non-CGI regions. Furthermore, NSD1-dependent H3K36 trimethylated domains can restrict PRC2-dependent H2K27me3 domains. In S/L-cultured ESCs, PRC2 is responsible for the establishment of bivalent domains at developmental genes before lineage commitment and long-term suppression of pluripotency genes upon differentiation.