Fig. 7.
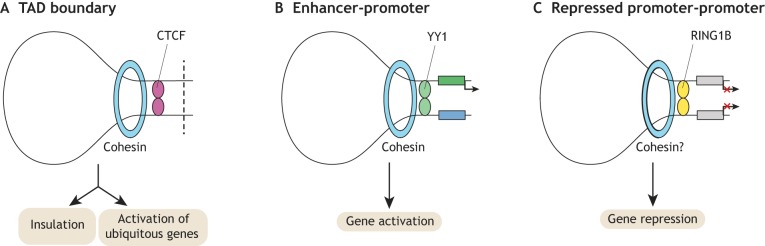
Chromatin looping factors in ESCs. Three factors were recently shown to be responsible, together with cohesin, for the formation of distinct chromatin loops in ESCs. (A,B) CTCF and YY1 both function together with cohesin in the formation of largely distinct loops, TAD boundaries (A) and enhancer-promoter loops (B), respectively. TAD boundaries are required for insulation of TADs and activation of ubiquitously expressed genes. Enhancer-promoter loops regulate gene transcription more directly. (C) RING1B plays a role in controlling contacts between repressed promoters, thereby contributing to repression of cognate genes.