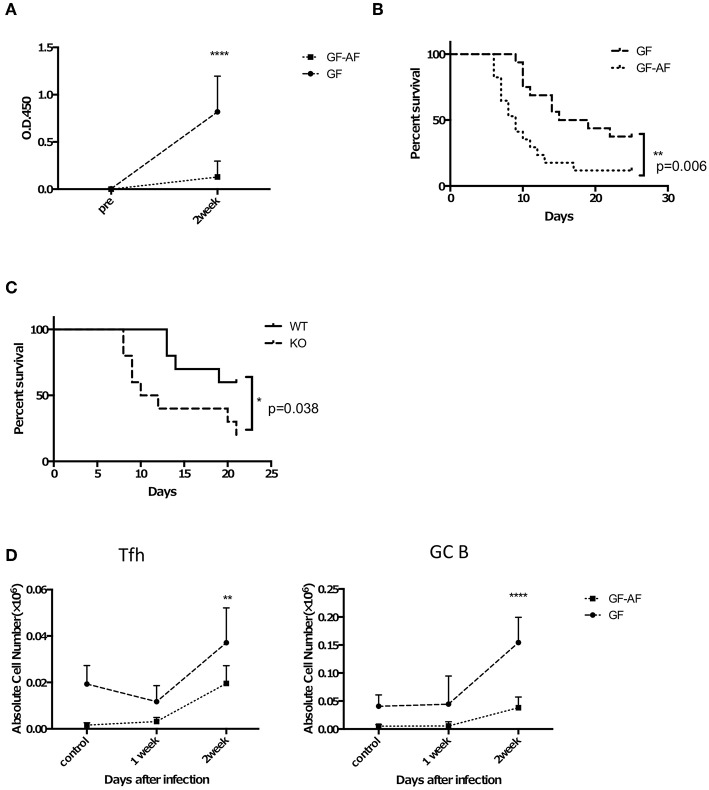
Figure 5.
GF-AF mice are more susceptible to S. Typhimurium infection than GF mice. Mice were orally infected with attenuated ΔaroA S. Typhimurium UF20. Two weeks later, mice were orally challenged with a virulent S. Typhimurium, χ3306. (A) The amount of S. Typhimurium-specific IgA in feces. Feces were collected from GF and GF-A mice before and 2 weeks after infection with UF20. Data are pooled from three independent experiments. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves after oral administration of χ3306. (GF; n = 16, GF-AF; n = 17). Data are pooled from three independent experiments. (C) AID knockout (n = 10) and their littermate wild-type (n = 10) mice were infected with S. Typhimurium in the same way as (B) and the survival curves are shown. Data are pooled from two independent experiments. (D) The numbers of Tfh and GF B cells in PP of GF and GF-AF mice before infection and 1 and 2 weeks after infection with UF20 S. Typhimurium (n = 5 or 6). Data are pooled from two independent experiments. Data are mean ± SD. Log rank test (B,C) and two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post-hoc test (B–D) were performed for statistical analysis. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.