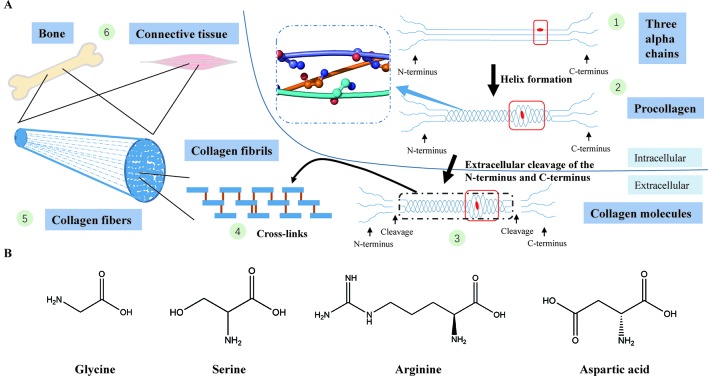
Figure 4.
(A) Type I collagen synthesis and application. (1) Formation of three alpha chains (two α1(I) chains and one α2(I) chain) (the red dot represents a Gly-substitution missense). (2) Triple helix formation (the blue dashed-line box displays the structure of the triple helix with a smooth loop model, in which all glycine residues are shown in ball-and-stick representation; the red box indicates abnormality of the triple helix after the Gly replacement). (3) Extracellular cleavage of the N-terminus and C-terminus (the red box indicates abnormality of the triple helix after the Gly replacement). (4) Cross-linking of type I collagen molecules. (5) Assembly of collagen fibrils to collagen fibers. (6) Collagen fibers participate in the formation of bone and connective tissues. (B) The chemical structural formula of four amino acids (glycine, serine, arginine, asparagic acid). Glycine, which has the smallest relative molecular mass, is the only amino acid with no sidechain.