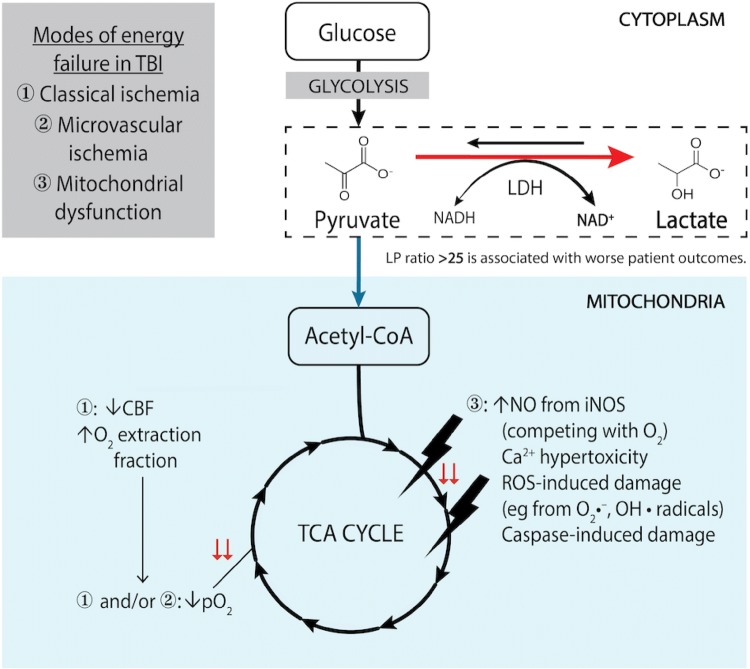
Fig. 2.
Summary of the mechanisms of energy failure in traumatic brain injury that lead to increased brain lactate: pyruvate ratio (LP ratio). The conversion of lactate to pyruvate is an oxygen-independent step, whereas oxidative phosphorylation and the tricarboxylic acid cycle are oxygen-dependent. Of note, reduced cerebral blood flow and increased oxygen extraction fraction, which characterize classical ischemia, are typically not seen in microvascular ischemia. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the TBI context can arise from multiple pathological processes, often concurrently (most common shown). Ca2+ ionized calcium, CBF cerebral blood flow, iNOS inducible nitric oxide synthase, LDH lactate dehydrogenase, NAD+ nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (oxidised form), NADH nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reduced form), NO nitric oxide, O2 oxygen, O2·−, superoxide radical, OH· hydroxyl radical, pO2 tissue oxygen saturation, ROS reactive oxygen species, TCA tricarboxylic acid cycle