Fig. 2.
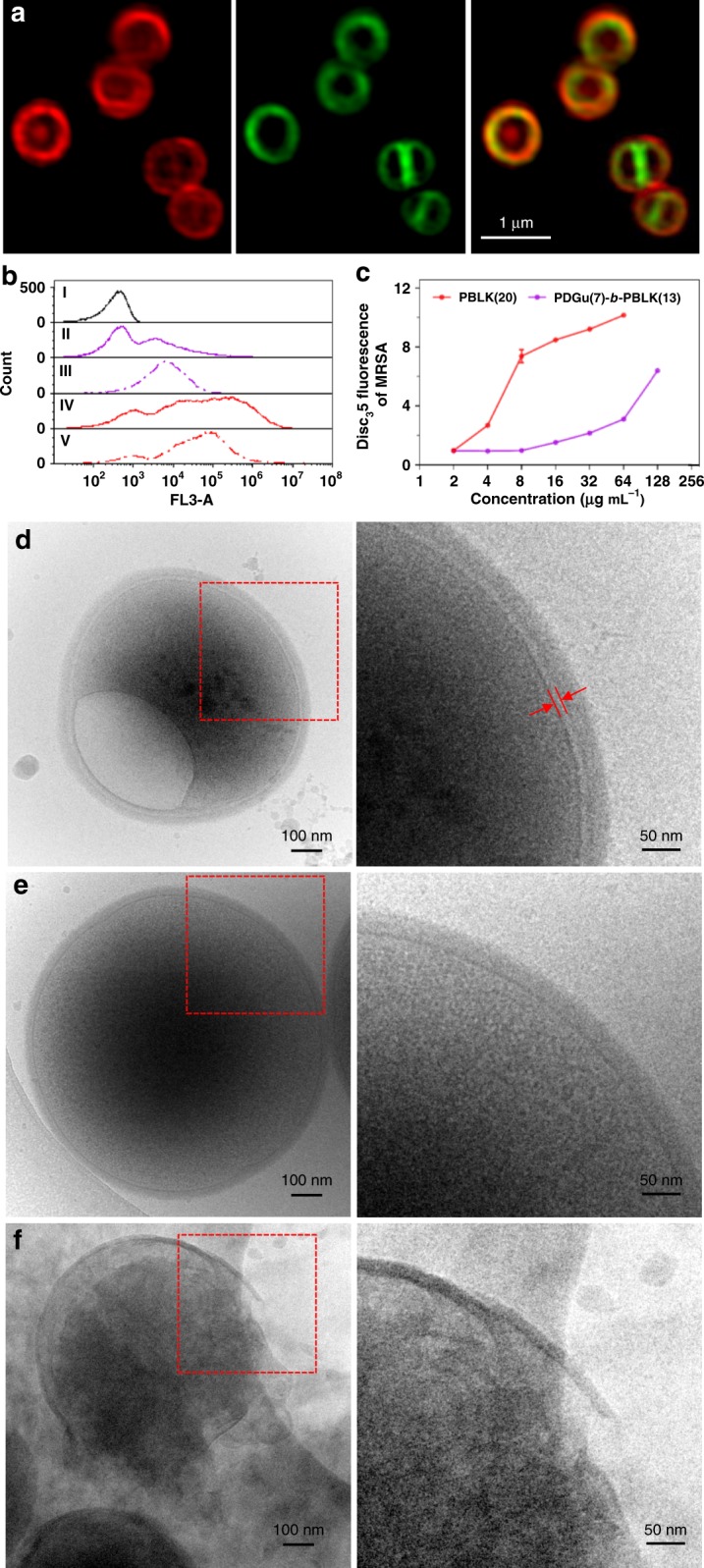
PDGu(7)-b-PBLK(13) targets bacterial cell envelope. It accumulates in MRSA USA300 cell envelope, mildly (at MIC) permeabilizing the membrane but significantly weakening cell wall/membrane attachment. a Confocal microscopy images of copolymer-treated MRSA USA300. From left to right: rhodamine-labeled copolymer channel, FM1-43-labeled bacteria membrane channel, superimposed images from both channels, respectively. b Flow cytometry study of propidium iodide-stained MRSA USA300. From top to bottom: live bacteria control, bacteria treated with 1× MIC PDGu(7)-b-PBLK(13), 4× MIC PDGu(7)-b-PBLK(13), 1× MIC PBLK(20), and 4× MIC PBLK(20). c DiSC35 membrane depolarization assay. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. d–f Cryo-TEM image of polymer treated MRSA USA300. d PDGu(7)-b-PBLK(13) treated bacteria with enlarged periplasmic space and vacuole structure formation; e untreated control; f PBLK(20)-treated bacteria with cell lysis
