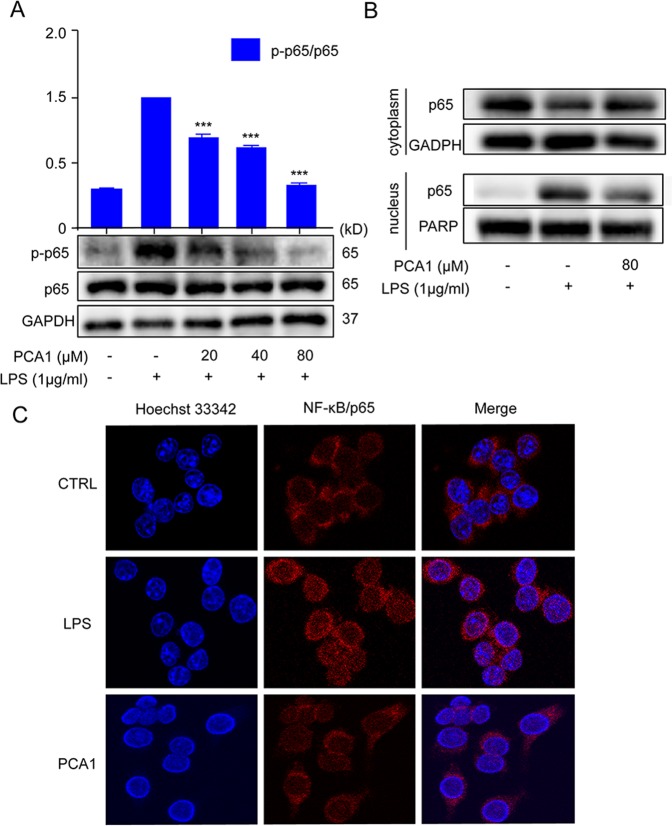
Figure 3.
PCA1 hindered LPS-induced NF-κB nuclear translocation. (A) RAW264.7 cells treated with PCA1 for 2 h were induced by LPS (1 μg/ml) for 2 h. p-p65 and p65 protein level was detected by Western blotting. (B) RAW264.7 cells were pretreated with PCA1 (80 μM) for 1 h and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 1 h. The localization of p65 in the cytoplasm and nucleus were detected by Western blotting. (C) RAW264.7 cells treated with for PCA1 for 2 h were included with LPS for 2 h. p65 translocation was determined using immunofluorescence analysis. The grouping of gels/blots cropped from different parts of the same gel (targets vs loading control) or different gels (phosphorylation). The full blots are shown in Supplementary Information. ***p < 0.001 versus the LPS group.