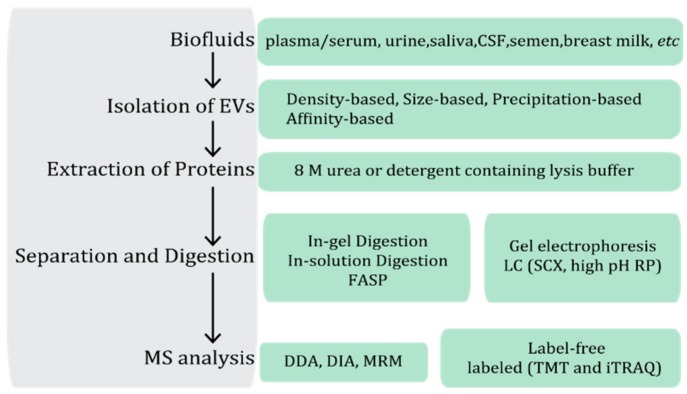
Figure 2.
A general workflow of mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomic extracellular vesicle (EV) study. EVs are firstly isolated from various biofluids, and EV proteins are extracted by adding detergent or non-detergent containing lysis buffer. The extracted EV proteins can be separated by gel electrophoresis and digested in-gel before MS analysis. Alternatively, digestion can be performed after protein extraction, and the generated peptides are either fractionated by liquid chromatography (LC) before MS analysis or directly subjected to MS analysis. The MS analysis can be conducted in data-dependent acquisition (DDA) or data-independent acquisition (DIA) for discovery EV studies or multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) for target EV studies. Differential expressed EV proteins also can be revealed by quantitative MS analysis via label-free or labeled quantitative proteomics. CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; FASP: filter aided sample preparation; SCX: strong cation exchange chromatography; RP: reverse phase chromatography; TMT: tandem mass tag; iTRAQ: isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation.