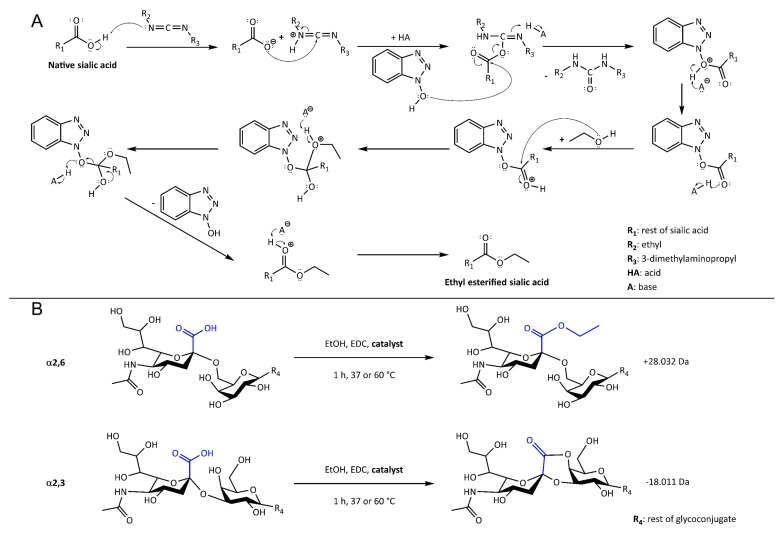
Figure 2.
Reaction mechanism (A) and scheme (B) for the linkage-specific sialic acid derivatization using EDC, ethanol and the array of catalysts (in A exemplified by the catalyst HOBt (Figure 1)). The expected reaction products included ethyl ester formation on α2,6-linked sialic acids, thereby gaining +28.032 Da (A and B, top), while α2,3-linked sialic acids formed lactones under the same conditions (−18.011 Da; B, bottom). Misconversion leads to ethyl esterification on α2,3-linked sialic acids or lactone formation on α2,6-linked sialic acids with the same changes in mass as indicated above.