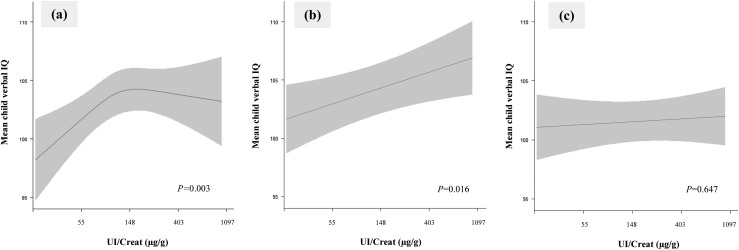
Figure 4.
Association of maternal iodine status during pregnancy with child verbal IQ score stratified by tertiles of gestational age. Continuous association, depicted as the mean child verbal IQ (black line) with 95% CI (gray area) was restricted to (a) the first 12 weeks of gestation (lowest tertile, median UI/Creat 116 µg/g; n = 2209); (b) from weeks 12 to 14 of gestation (middle tertile, median UI/Creat 147 µg/g; n = 1776); and (c) later than week 14 of gestation (highest tertile, median UI/Creat 157 µg/g; n = 1879). Models are adjusted for gestational age, child sex, maternal ethnicity/country of birth, maternal education, parity, maternal age, prepregnancy body mass index, and smoking during pregnancy. The P value was provided by an ANOVA test of the null hypothesis that mean child verbal IQ was similar across the whole range of the natural logarithm of UI/Creat.