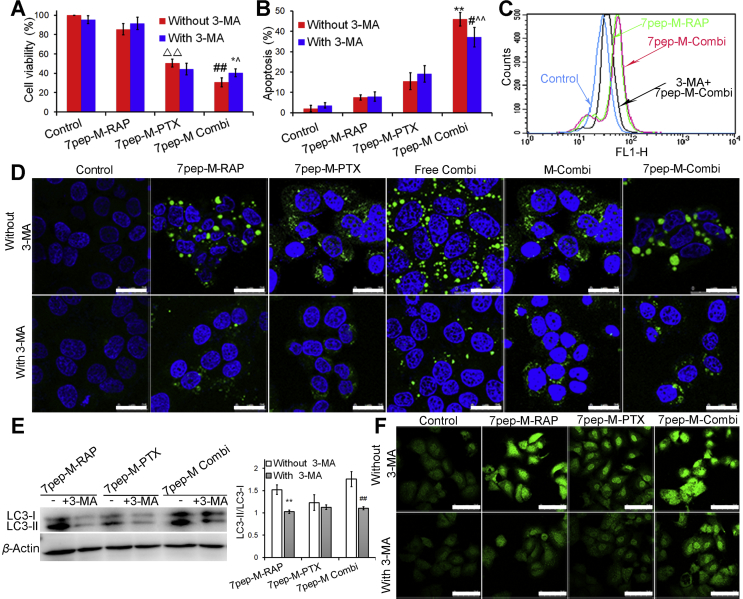
Figure 5.
The inhibition effect of autophagy inhibitor 3-MA on cytotoxicity, apoptosis and intracellular autophagic vesicular accumulation. (A) The effect of 3-MA on the cytotoxicity induced by 7pep-M-PTX in single or in combination with 7pep-M-RAP (mean ± SD, n = 6). ▵▵P < 0.01 vs control without 3-MA; ##P < 0.01 vs 7pep-M-PTX without 3-MA; *P < 0.05 vs 7pep-M-Combi without 3-MA; ˆP < 0.05 vs 7pep-M-PTX without 3-MA. (B) Quantitative analysis of in vitro cell apoptosis based on flow cytometric plots (mean ± SD, n = 4). Each bar represents the sum of early apoptotic cells and late apoptotic cells. **P < 0.01 vs 7pep-M-PTX without 3-MA; #P < 0.05 vs 7pep-M-Combi without 3-MA; ˆˆP < 0.01 vs 7pep-M-PTX without 3-MA. (C) The effect of 3-MA on the Cyto-ID specifically labeled autophagic vesicles detected by flow cytometry. (D) The inhibition effect of 3-MA on the Cyto-ID dye specifically labeled autophagic compartments. Images showed the colocalization of the Cyto-ID fluorescence dye (green) and Hoechst 33342 (blue). The white scales represent 25 μm. (E) Levels of LC3-II to LC3-I measured by western-blot, and the ratios of LC3-II to LC3-I were calculated by comparing the band densities (mean ± SD, n = 3). **P < 0.01 vs Control. ##P < 0.01 vs 7pep-M Combi without 3-MA. (F) The inhibition effect of 3-MA on the LC3B labeled autophagic vesicles. The white scale bars represent 75 μm.