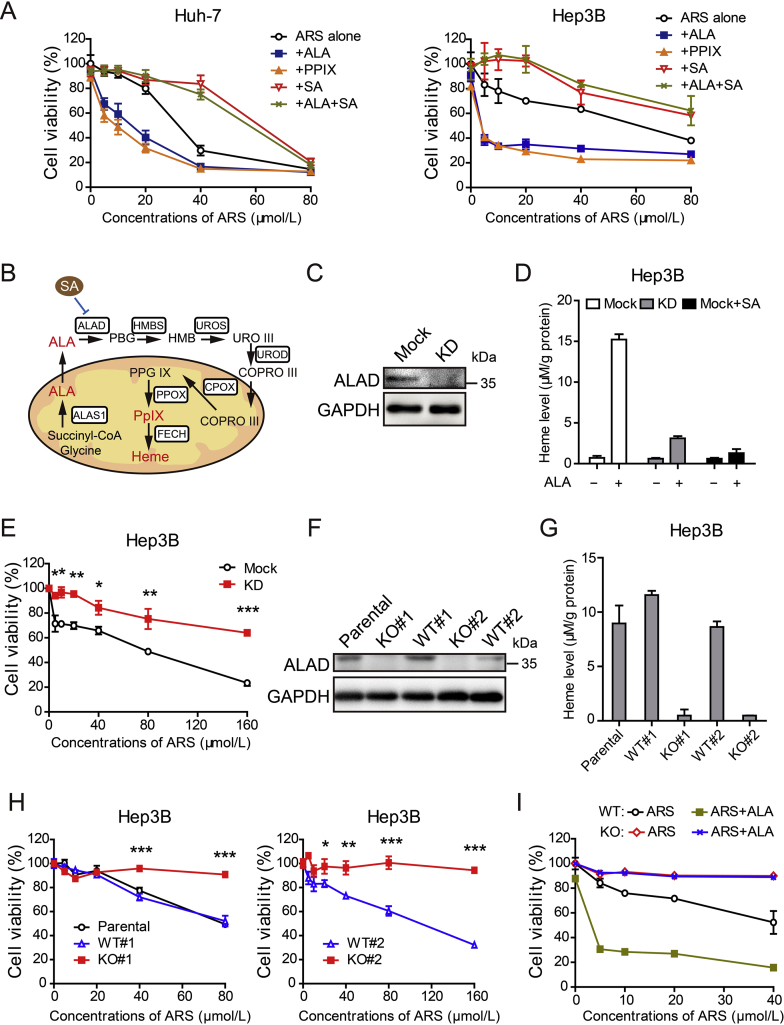
Figure 3.
Cytotoxicity of ARS depends on heme synthesis. (A) Huh-7 cells (left) and Hep3B cell (right) were exposed to various concentrations of ARS (0, 5, 10, 20, 40 and 80 μmol/L) alone or in combination with ALA (1 mmol/L), PpIX (5 μmol/L) or succinyl acetone (SA, 0.5 mmol/L) for 48 h followed by CCK-8 assay. Error bars represent SD of quadruplicate experiments. (B) Schematic representation of heme biosynthetic pathway and its exogenous modulators. (C) Hep3B cells were transfected with lentiCRISPR-sgRNA-ALAD or mock and ALAD knockdown was verified by Western blot assay. (D) ALAD knockdown cells and mock cells in the presence or absence of 0.5 mmol/L SA were treated with 0.5 mmol/L ALA or vehicle for 4 h for whole cell heme measurement (n = 4). (E) Cell viability was determined by CCK-8 assay after 72 h treatment with ARS as indicated. Error bars represent SD of triplicate experiments. Asterisks, ALAD KD vs Mock; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (Student's t-test). (F) Western blot analysis of ALAD in Hep3B parental cells, WT and KO clones. Western blot shows ALAD detection from one of three independent experiments. (G) ALAD KO cells, WT cells and parental cells were administered with 0.5 mmol/L ALA for 4 h for whole cell heme measurement (n = 3). (H) Cell viability was measured by MTT assay after 72 h treatment with ARS as indicated. Error bars represent SD of triplicate experiments. Asterisks, KO vs WT; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (Student's t-test). (I) ALAD KO cells and WT cell were treated with various concentrations of ARS alone or in combination with ALA (1 mmol/L) for 48 h. Cell viability was performed by CCK-8 assay. Error bars represent SD of triplicate experiments.