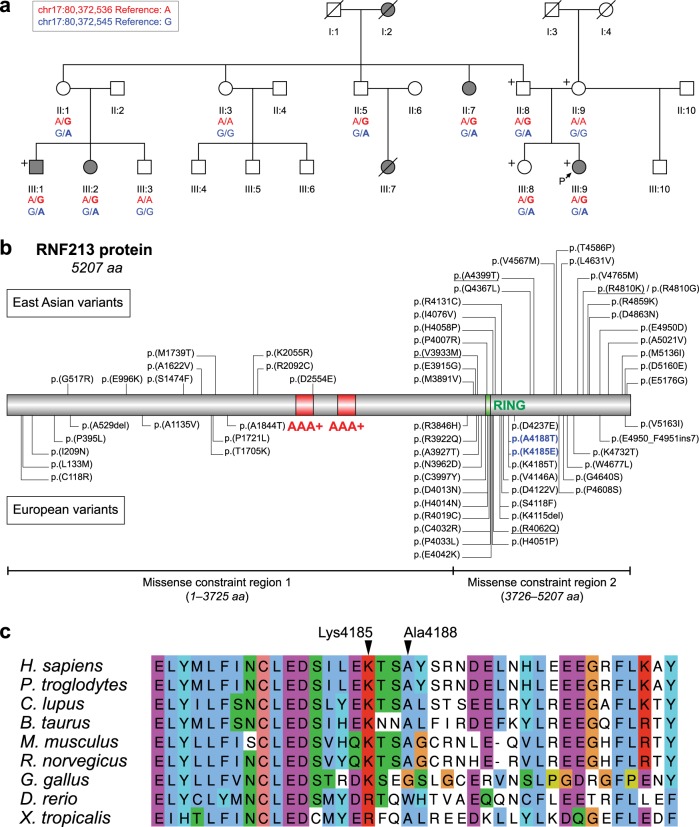
Fig. 1. Novel missense variants in the RNF213 gene from a European family with MMD.
a Pedigree of the family. The genotypes of the two RNF213 variants are shown below each family member for which a DNA sample was available, where red refers to the status of the missense variant c.12553A>G (p.(Lys4185Glu)), and blue refers to the status of the missense variant c.12562G>A (p.(Ala4188Thr)) (reference allele/alternate allele). Filled symbols denote affected individuals, unfilled symbols denote unaffected individuals, and slashed lines denote deceased. Five individuals who were whole-exome sequenced are denoted with a plus sign. P, proband. The genotypes of other family members were obtained with Sanger sequencing. b The domain structure of the RNF213 protein based on14 and variants previously reported in East Asian and European MMD patients1,2,5,11–13,15–20 (shown above and below the protein, respectively). The variants reported for both populations are underlined, and the ones identified in this study are shown in blue. Two distinct regions with different missense constraints identified by Samocha and coworkers6 are shown below the protein. c Conservation of amino acid residues affected by the c.12553A>G (p.(Lys4185Glu)) and c.12562G>A (p.(Ala4188Thr)) variants. AAA+, ATPases associated with various cellular activity domains; RING, RING-finger domain