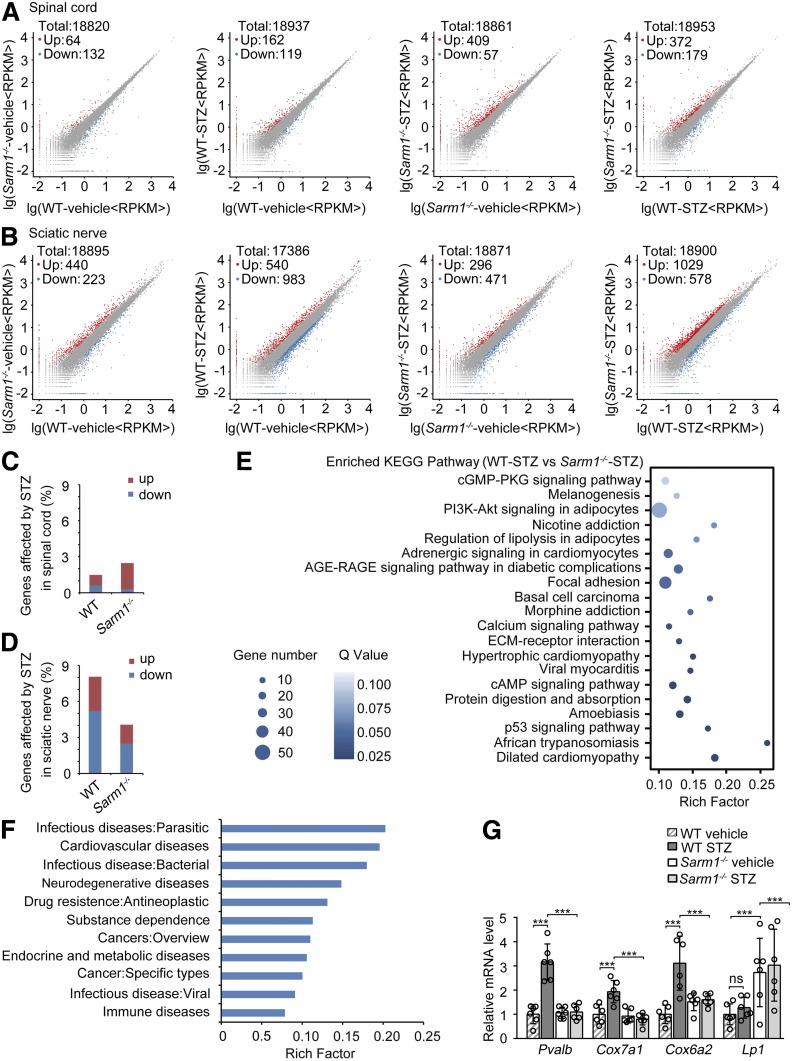
Figure 7.
Sarm1 gene deficiency diminishes the changes of gene expression profile induced by STZ in the sciatic nerve. Scatter plot comparing the differentially expressed genes detected by high-throughput sequencing in spinal cord (A) and sciatic nerve (B) between wild-type (WT) and Sarm1−/− mice after 5-day consecutive injection with vehicle or STZ and for the subsequent 25 weeks. C and D: The percentage of genes affected by STZ treatment in spinal cord (C) and sciatic nerve (D) of WT and Sarm1−/− mice as described in A and B. E: The top 20 significantly enriched KEGG pathway of the differentially expressed genes in sciatic nerve between WT and Sarm1−/− mice treated with STZ. F: The differentially expressed genes in sciatic nerve between WT and Sarm1−/− mice treated with STZ enriched in human diseases. G: Top four abundant genes enriched in neurodegenerative diseases in F were validated by quantitative PCR. n = 6 for each group. ***P < 0.001. ECM, extracellular matrix; RPKM, read per kilobase per million mapped reads.