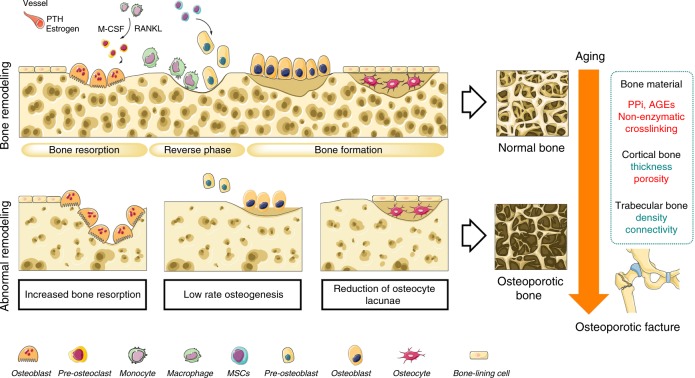
Fig. 1.
Static and dynamic changes in osteoporotic bone. An osteoporotic fracture is the macroscopic result of microstructural alterations that change the response of bone to the applied load. The aging process in osteoporotic bone would lead to overaccumulation of PPi, AGEs, and nonenzymatic crosslinking of collagen, which disturb the normal organization of bone material. With the increase of bone resorption and low rate osteogenesis, the osteocyte lacunae reduction leads to decreased trabecular thickness and more porous cortical bone. PTH parathyroid hormone, M-CSF macrophage colony-stimulating factor, RANKL receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand, PPi inorganic pyrophosphate, AGEs advanced glycation end-products, MSCs mesenchymal stem cells. “Red” refers to upregulation; “Green” refers to downregulation