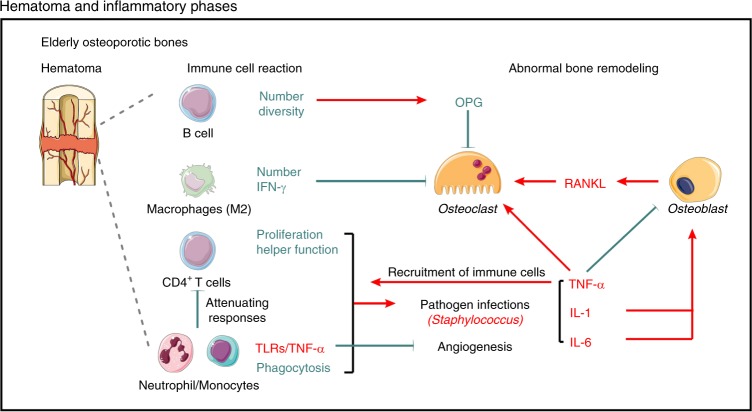
Fig. 2.
Osteoimmunology in elderly osteoporotic bones. Hematoma and inflammatory phases are the immediate reactions to a fracture. The limited inflammatory response at the fracture site is essential to initiate repair processes and mobilize all the required factors involved in the early bridging of the fracture gap, especially in indirect bony unions without rigid fixation. The high RANKL/OPG ratio caused by aging-related inflammation and the lack of mature B cells is associated with the hyperactivation of osteoclastogenesis and aggravation of bone resorption in elderly patients with bone loss, which increases the incidence of intra- or postoperative further fractures. OPG osteoprotegerin, IFN-γ interferon gamma, RANKL receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand, TLRs toll-like receptors, TNF-α tumor necrosis factor alpha, IL-1 interleukin-1, IL-6 interleukin-6. “Red” refers to upregulation; “Green” refers to downregulation