Fig. 2.
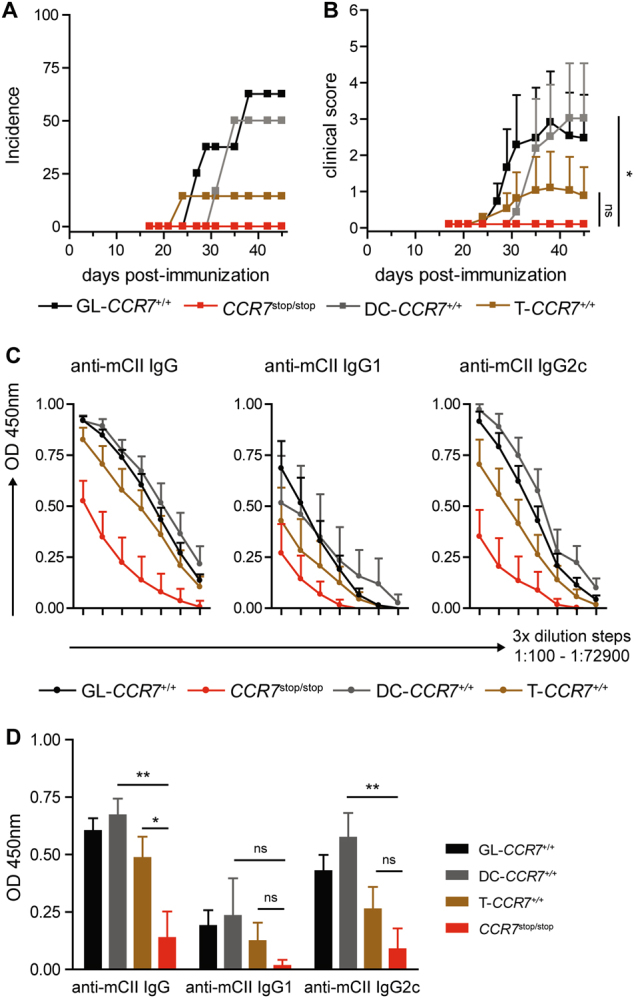
CCR7 expression on DCs is critical for the development of CIA. a Incidence and score (b) of CIA in GL-CCR7+/+, T-CCR7+/+, DC-CCR7+/+, and CCR7stop/stop mice. The data are shown from 6–8 mice per group. The data in (b) are the mean ± SEM. Areas under the curve (AUC) calculated from the CIA scores were compared for statistical significance (Student’s t-test) *P < 0.05; c Levels of anti-murine-CII IgG, IgG1c and IgG2c were measured in serially diluted serum samples (3-fold dilution steps, 1:100–1:72900) from GL-CCR7+/+, T-CCR7+/+, DC-CCR7+/+, and CCR7stop/stop mice upon CIA induction. d Levels of anti-murine-CII IgG, -IgG1, and -IgG2c shown in (c) at a serum dilution of 1:2700 were compared for statistical significance. The data in (c, d) are presented as the mean ± SEM from 6–10 mice per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
