Fig. 5.
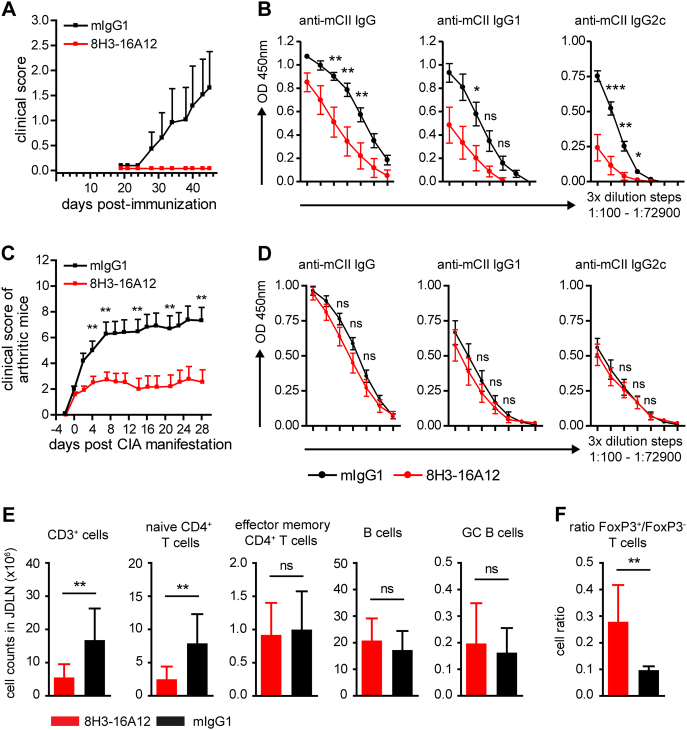
Treatment with 8H3-16A12 inhibits CIA development. a CIA score of GL-CCR7+/+ mice that were injected i.p. with 20 mg/kg 8H3-16A12 or 20 mg/kg mIgG1 control Ab every 12 days starting at day 4 before CIA induction. The results are shown from ≥18 mice per group. b Sera were collected from mice shown in (a), and levels of anti-murine-CII IgG, IgG1, and IgG2c were measured in serially diluted serum samples (3-fold dilution steps, 1:100–1:72900). The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. c CIA score of GL-CCR7+/+ mice that were treated upon manifestation of arthritis every 10 days with i.p. injections of 20 mg/kg 8H3-16A12 or 20 mg/kg mIgG1 control Ab. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM from ≥11 mice per group. d Anti-murine-CII IgG, IgG1, and -IgG2c levels were measured in serially diluted serum samples from mice shown in (c) (3-fold dilution steps, 1:100–1:72900). The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. e Cell counts of the indicated immune cell subsets and the ratio of FoxP3+/FoxP3- T cells f were assessed upon termination of the observation period in mice shown in (c) in JDLN by flow cytometry. Naïve CD4+ T cells were gated as CD62L+ CD44−, effector memory CD4+ T cells as CD62L− CD44+ and GC B cells as B220+ Fas+ cells. The data are presented as the mean ± SD from ≥11 mice per group. Ns not significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001