Figure 2.
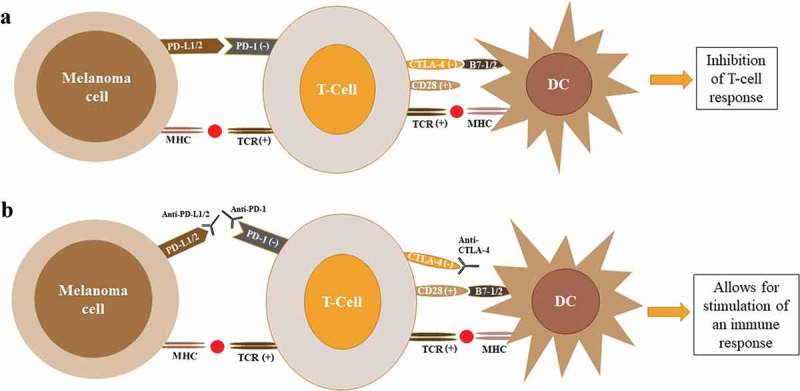
Regulation of T-cell response by CTLA4 and PD1. (A) T-cell activation by dendritic cells requires signaling by both the MHC and CD28 complexes. Binding of the CTLA4 to B7-1/2 (CD80/86) suppresses T-cell activation and acts as a feedback mechanism to prevent ongoing immune response. Binding to the MHC class I complex on melanoma cells leads to T-cell activation. After persistent activation, T-cells upregulate PD-1 expression. When PD-1 binds to the PD-L1/2 expressed by tumor cells, this leads to deactivation of T-cells. (B) Antibodies against CTLA4, PD1 or PD-L1/2 prevent binding to associated ligands leading to activation of T-cells and stimulation of an immune response to tumor cells. Abbreviations: DC, dendritic cell; CTLA4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; PD1, programmed death 1; TCR, T-cell receptor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; PD-L2, programmed death-ligand 2.
