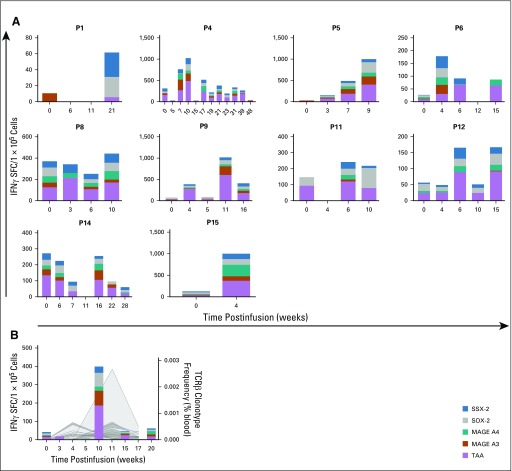
FIG 4.
Antigen spreading and T-cell persistence postinfusion in responders. (A) Interferon gamma (IFNγ) enzyme-linked immunospot assay was used to evaluate antitumor immunity to the targeted antigens (Wilms tumor 1, preferentially expressed antigen of melanoma, survivin), as well as four nontargeted antigens commonly identified in solid tumors (MAGE A3, MAGE A4, SOX-2, SSX-2). Ten of 11 responders demonstrated evidence of antigen spreading while receiving tumor-associated antigen (TAAs) cytotoxic T cell infusions. Patient 1 (P1) did not show increased specificity for targeted or nontargeted antigens until after disease progression at week 12. (B) Increased specificity to targeted and nontargeted antigens correlated with the expansion of unique T-cell receptor (TCR) clonotypes as detected by TCR sequencing in P10, a responder.