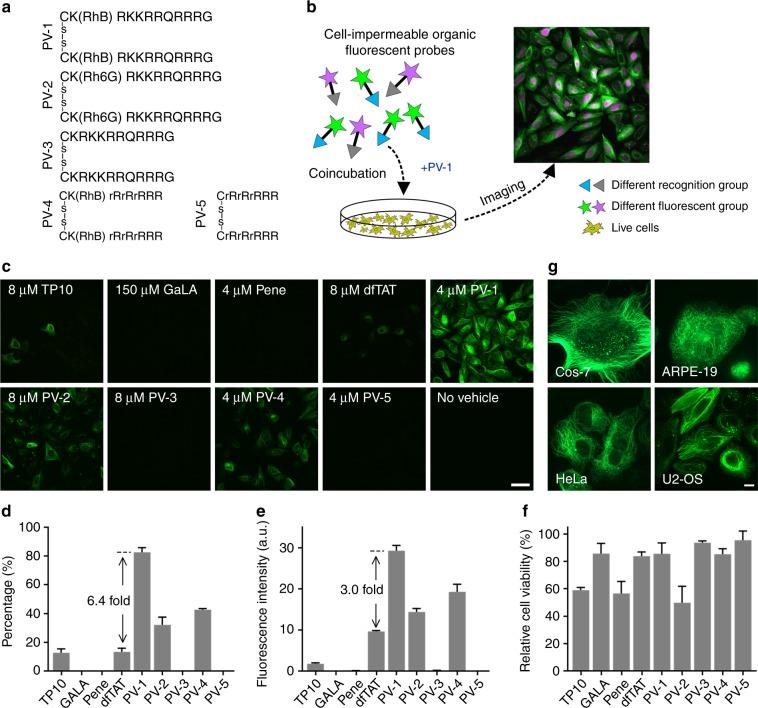
Fig. 1. PV-1 efficiently delivers Tubulin-FITC into live cells.
a The chemical structures of the peptide vehicles. r, d-Arginine; -s-s-, a disulfide bond; RhB, rhodamine B; Rh6G, a rhodamine derivative (fig. S1). b A schematic of the intracellular delivery of PV-1. c Confocal microscopy images of live U-2 OS cells after a 1-h coincubation with Tubulin-FITC (5 μM) and the indicated peptide vehicles at the indicated optimal concentrations for probe delivery. Scale bar: 50 μm. d Percentages of live cells labeled by Tubulin-FITC after a 1-h coincubation with the indicated peptide vehicles (mean + s.d., n = 1000 cells from triplicate experiments). e The mean fluorescence intensity of Tubulin-FITC inside one cell after a 1-h coincubation with Tubulin-FITC (5 μM) and the indicated peptide vehicles (mean + s.d., n = 1,000 cells from triplicate experiments), a.u.: arbitrary units. f U-2 OS relative cell viability after a 1-h incubation with the indicated peptide vehicles. The error bars represent the standard deviations of triplicate experiments. The concentrations of the peptide vehicles used in (d–f) were the same as those used in (c). g Confocal microscopy images of various live cells after a 1-h coincubation with Tubulin-FITC (5 μM) and PV-1 (4 μM). Scale bar: 10 μm