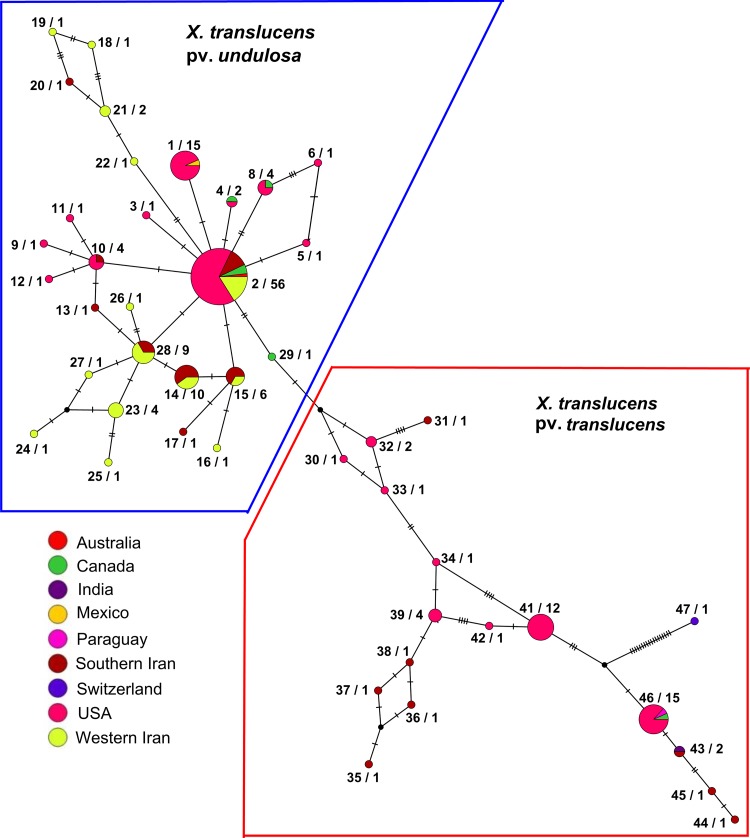
FIG 2.
TCS multilocus haplotype (MH) network generated using the POPART program from the concatenated partial sequences of four housekeeping genes (dnaK, fyuA, gyrB, and rpoD) in 178 Xanthomonas translucens strains from Iran and seven countries around the globe. The size of a circle indicates the relative frequency of sequences belonging to a particular MH. Hatch marks along the branches indicate the numbers of mutations. Each color indicates a different geographic area. To provide precise insight into the diversity of the pathogen, strains isolated in southern Iran and western Iran were considered distinct groups. The number to the left of a slash represents the MH number (Table S1), while the number to the right of a slash indicates the number of strains in a given MH. Xanthomonas translucens pv. undulosa strains are surrounded by blue lines, while X. translucens pv. translucens strains are surrounded by red lines. MH2, consisting of 56 X. translucens pv. undulosa strains, was considered the founder genotype of the pathovar as confirmed by the phylogeographic analyses using the eBURST program (Fig. S5).