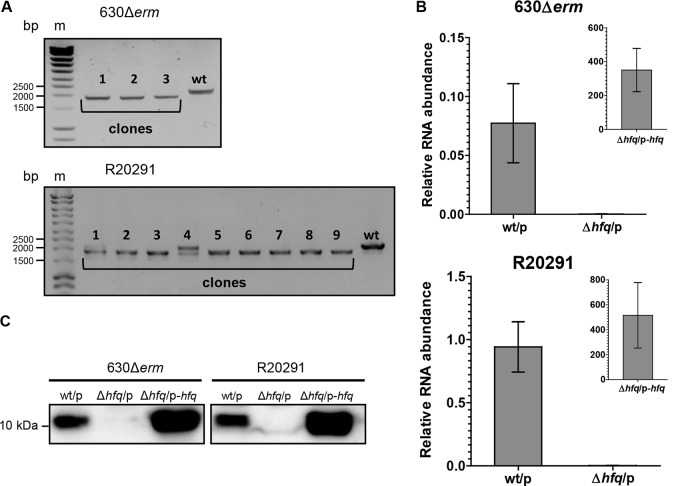
FIG 4.
Validation of hfq deletion mutants. (A) PCR analysis of the C. difficile clones which lost the plasmid after genome editing. The 2,151-bp PCR bands correspond to the wild-type genotype; the 1,893-bp PCR bands correspond to the mutant genotype. For the R20291 strain, both the wild-type and mutant copies were detected with clone 4 (lane 4); this clone was discarded from further analysis. Lanes m, molecular mass markers. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of the wild-type and Δhfq mutant strains carrying an empty pRPF185Δgus (the wt/p and Δhfq/p strains, respectively) and the complemented Δhfq C. difficile strain (the Δhfq/p-hfq strain). mRNA levels are relative to those of 16S rRNA. (C) Western blot analysis of the wt/p, Δhfq-p, and Δhfq/p-hfq C. difficile strains. As loading controls, InstantBlue dye-stained protein gels were used (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material).