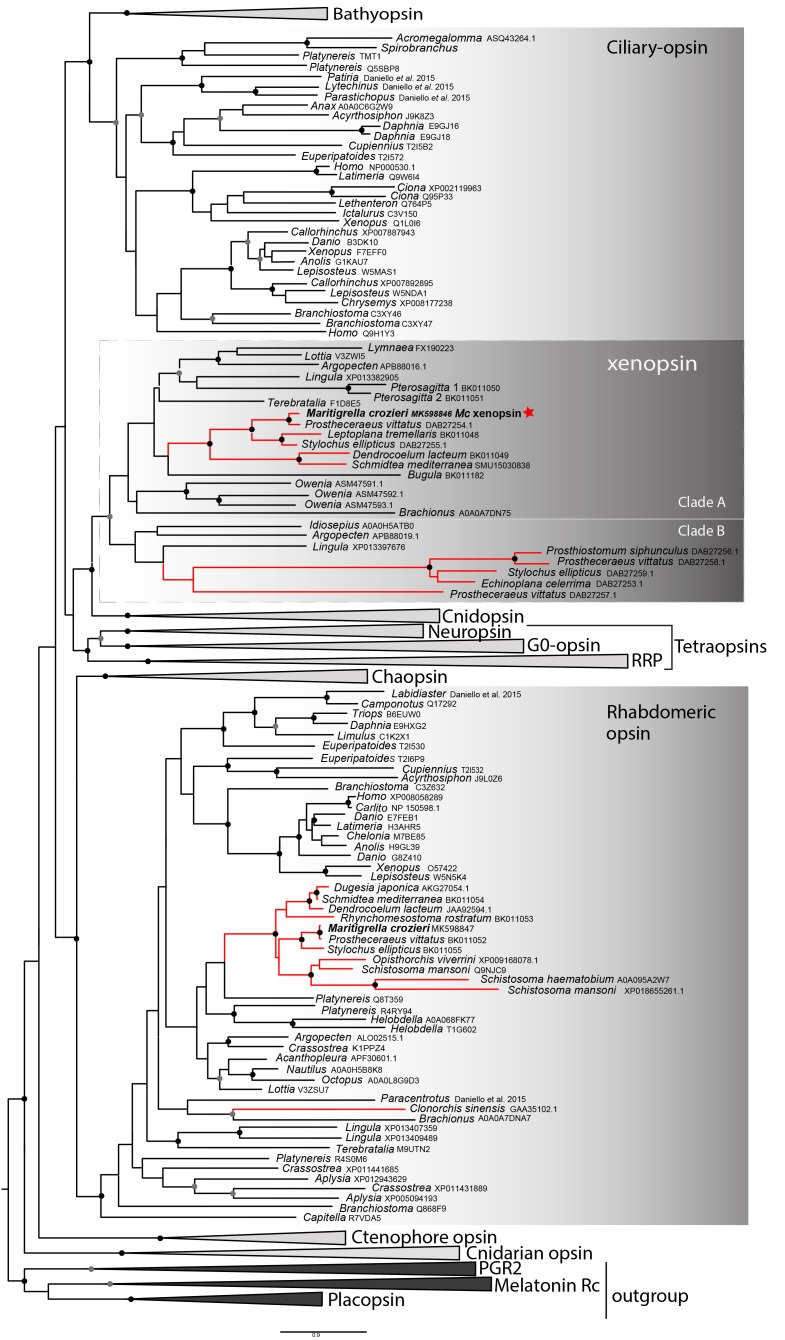
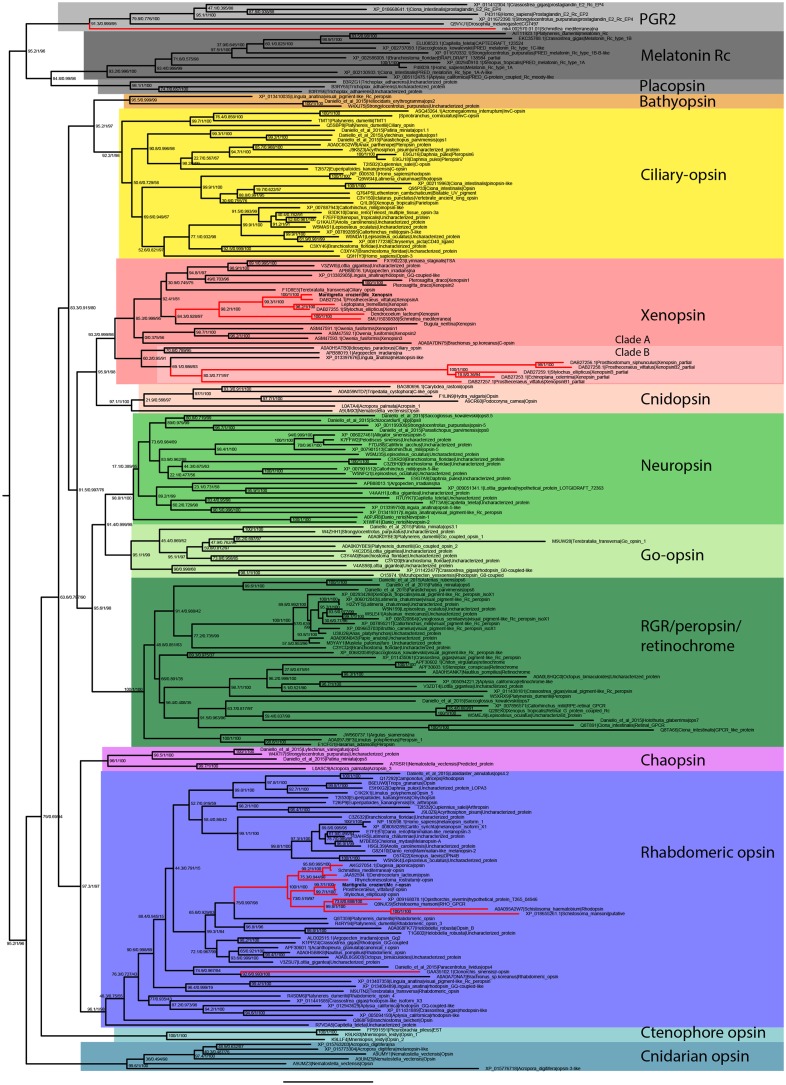
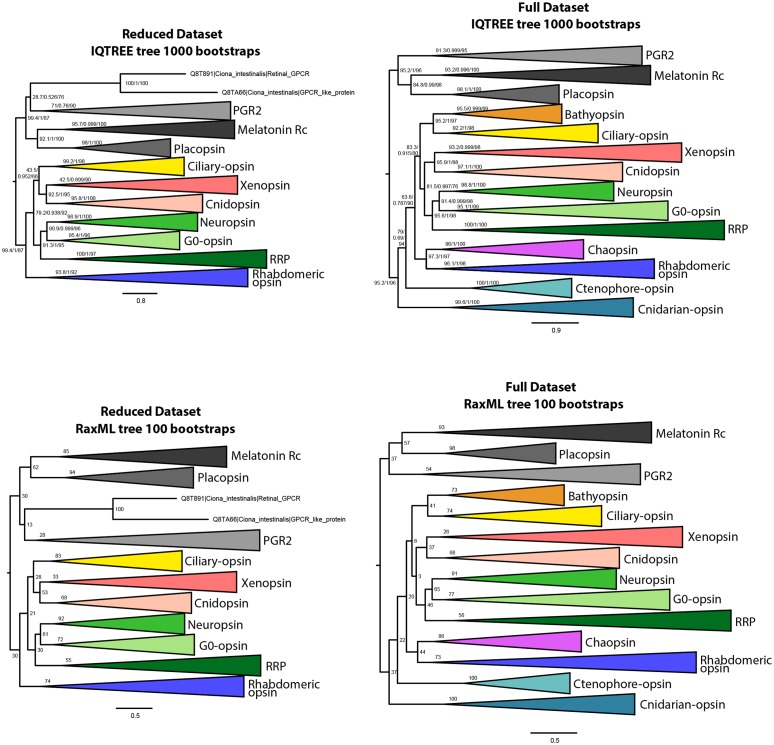
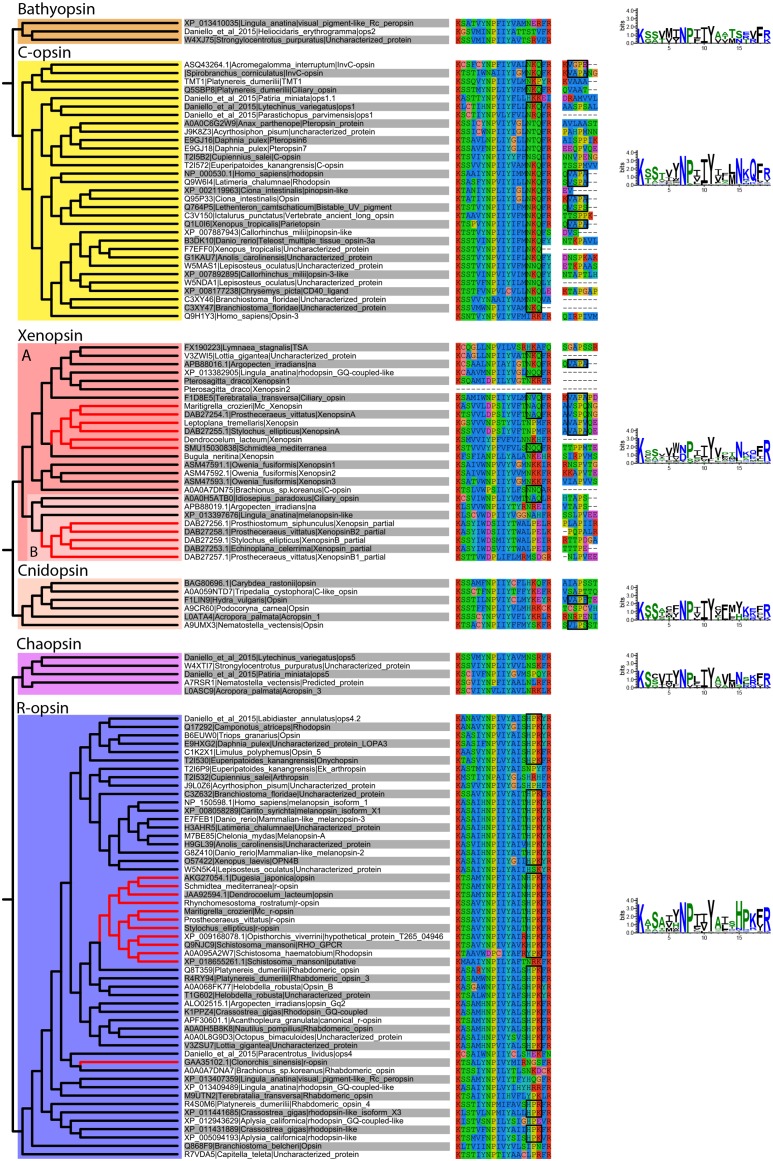
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of metazoan opsins supports flatworm ciliary-like opsins as xenopsins and confirms a clade of flatworm rhabdomeric opsins.
Support for nodes is calculated using 1000 Ultrafast bootstrap replications as well as 1000 SH-aLRT replicates and approximate aBayes single Branch testing. Black dots indicate nodes with support values for three tests ≥ 95% (0.95 for SH-aLRT replicates). Gray dots indicate nodes with support values for three tests ≥ 90% (0.90 for SH-aLRT replicates). Scale bar unit for branch length is the number of substitutions per site. Branches in red correspond to flatworm opsin sequences. See Figure 1—figure supplement 1 for uncollapsed tree and Figure 1—source data 1 for gene accession numbers. The new xenopsin sequences we found in polyclad and triclad flatworms, plus a bryozoan and chaetognath, all fall within clade A of the xenopsins.