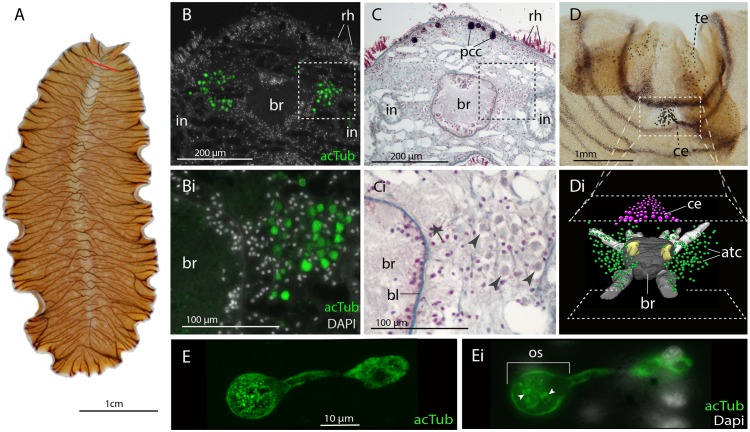
Figure 3. Acetylated tubulin staining identifies two dense clusters of extraocular cells, possible ciliary photoreceptors (CPR), either side of the adult brain.
(A) Live adult, red line shows plane of cross section in B-C. (B and C) Consecutive sections showing; (B) two clusters of acetylated tubulin+ cells and; (C) their distribution between the brain (br) (which is encapsulated in a basal lamina, bl) and intestinal branches (in) (n = 5 individuals). Bi and Ci) Close up showing that these cells (arrowheads) are embedded in extracellular matrix in close proximity to the main nerve tracts (arrow). Pigment cup cells (pcc), rhabdites (rh). (D) Anterior end of adult showing pigmented eyes above the brain (cerebral eyes, ce) and on the tentacles (tentacular eyes, te). (Di) Schematised distribution of acetylated tubulin+ cells (act) and cerebral eyes on a micro-CT reconstruction of the brain and main anterior (white), posterior (gray), and two of the optic (yellow) nerve tracts. (E) Confocal projection of a putative CPR and, Ei) an optical slice of the same cell showing cilia projecting into the intra-cellular vacuole or phaosome (arrowheads) in the outer segment (os).