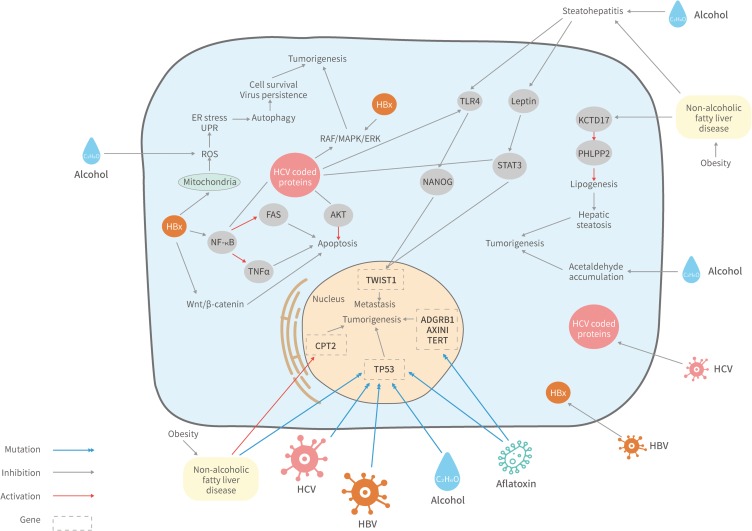
Figure 1.
Signaling pathways affected by the etiological factors of HCC. HBV/HCV infection, alcohol consumption, aflatoxin exposure, NAFLD and metabolic disorders may trigger HCC by manipulating diverse signaling pathways.
Abbreviations: ADGRB1, adhesion G protein-coupled receptor B1 gene; AKT, protein kinase B; CPT2, carnitine o-palmitoyltransferase 2 gene; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; FAS, fas receptor; KCTD17, potassium channel tetramerization domain containing 17; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; NANOG, homeobox protein; PHLPP2, PH domain and leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor; TWIST1, twist-related protein 1; UPR, unfolded protein response.