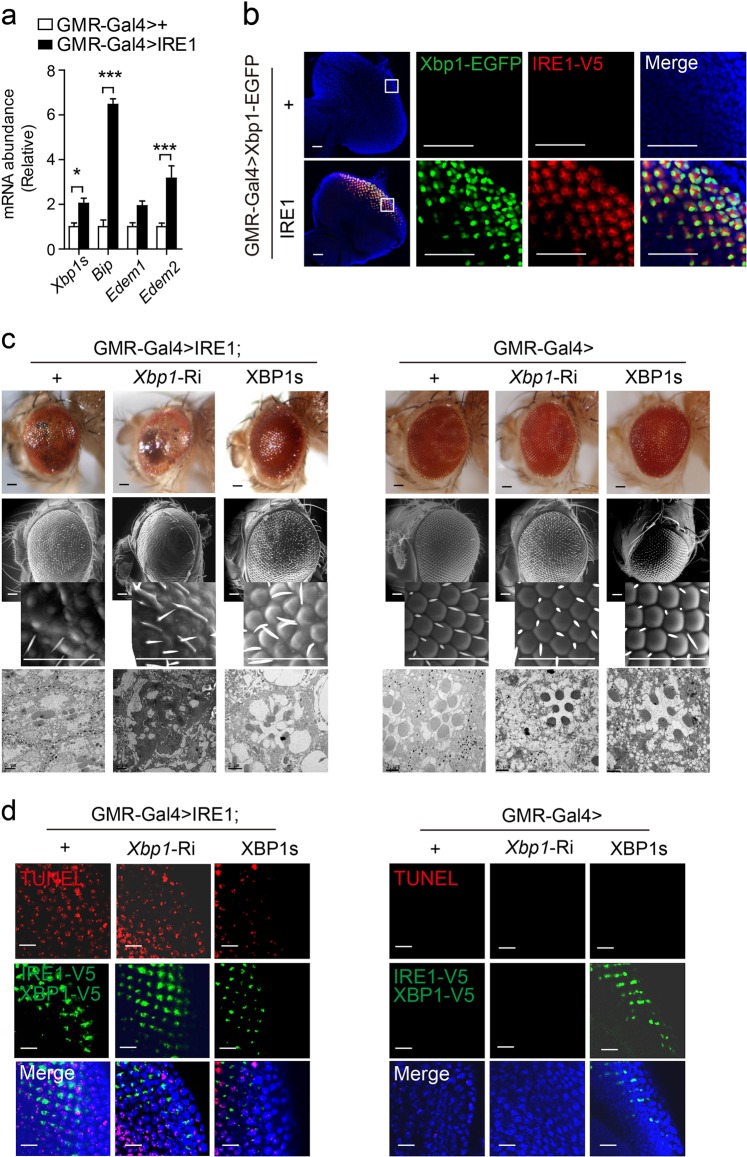
Fig. 4. IRE1 induces neuron death in an XBP1-independent fashion.
a Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Xbp1 mRNA splicing and the mRNA abundance of Bip, Edem 1 and Edem2 from the head lysates of adult GMR-Gal4 > + and GMR-Gal4 > IRE1 flies. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. (n = 30 flies/genotype; three independent experiments). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 by Student’s t test. b Confocal microscopy analysis of eye discs from 3rd instar larvae of the GMR-Gal4 > Xbp1-EGFP versus GMR-Gal4 > Xbp1-EGFP;IRE1 line. Representative images are shown for Xbp1 mRNA splicing-directed EGFP expression, along with IRE1 immunostaining with anti-V5 antibody and DAPI staining for eye discs with the enlarged regions indicated (n = 20 flies/genotype). Scale bar represents 30 µm. c Representative light microscopy (top), SEM (middle, with enlarged sections) and TEM (bottom) images of external eyes from adult GMR-Gal4 > IRE1, GMR-Gal4 > IRE1; Xbp1-Ri and GMR-Gal4 > IRE1; XBP1s flies versus GMR-Gal4 > +, GMR-Gal4 > Xbp1-Ri and GMR-Gal4 > XBP1s flies (n = 5–8 flies/genotype). Scale bar represents 50 µm. d Cell death analysis by TUNEL of eye discs from 3rd instar larvae of the indicated lines. Shown are representative images of TUNEL and DAPI staining along with IRE1 immunostaining (n = 20 flies/genotype). Scale bar represents 10 µm