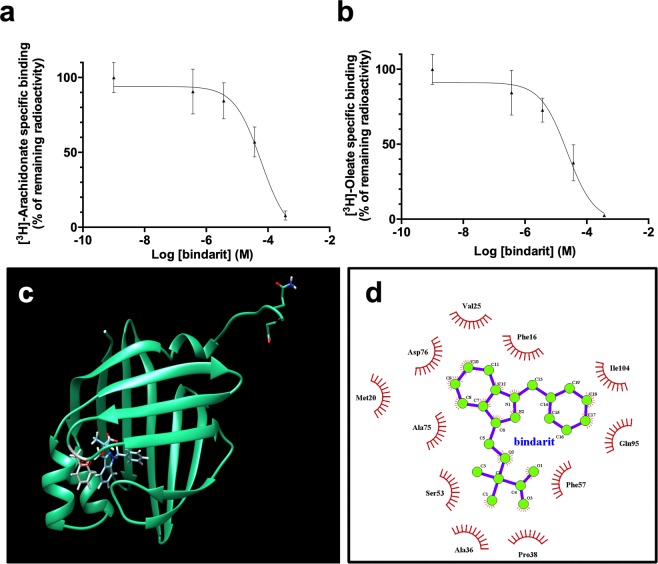
Figure 2.
In vitro and in silico studies of the physical interaction between human FABP4 and bindarit. Displacement of [3H]-arachidonic (a) and [3H]-oleic acid (b) from the binding site of human FABP4 by bindarit. Displacement curves were fit to a one-site model with Ki values of 19 μM and 60 μM for arachidonate and oleate, respectively. The graphed points represent the means ± S.D. of 2 independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. (c) Bindarit has a binding mode similar to that of ibuprofen in the active site of human FABP4. Grey: residue Phe57, involved in the binding of small molecules. (d) 2D plot representation of the bindarit’s interactions with amino acid residues in the fatty acid binding pocket of the human FABP4.