FIG 4.
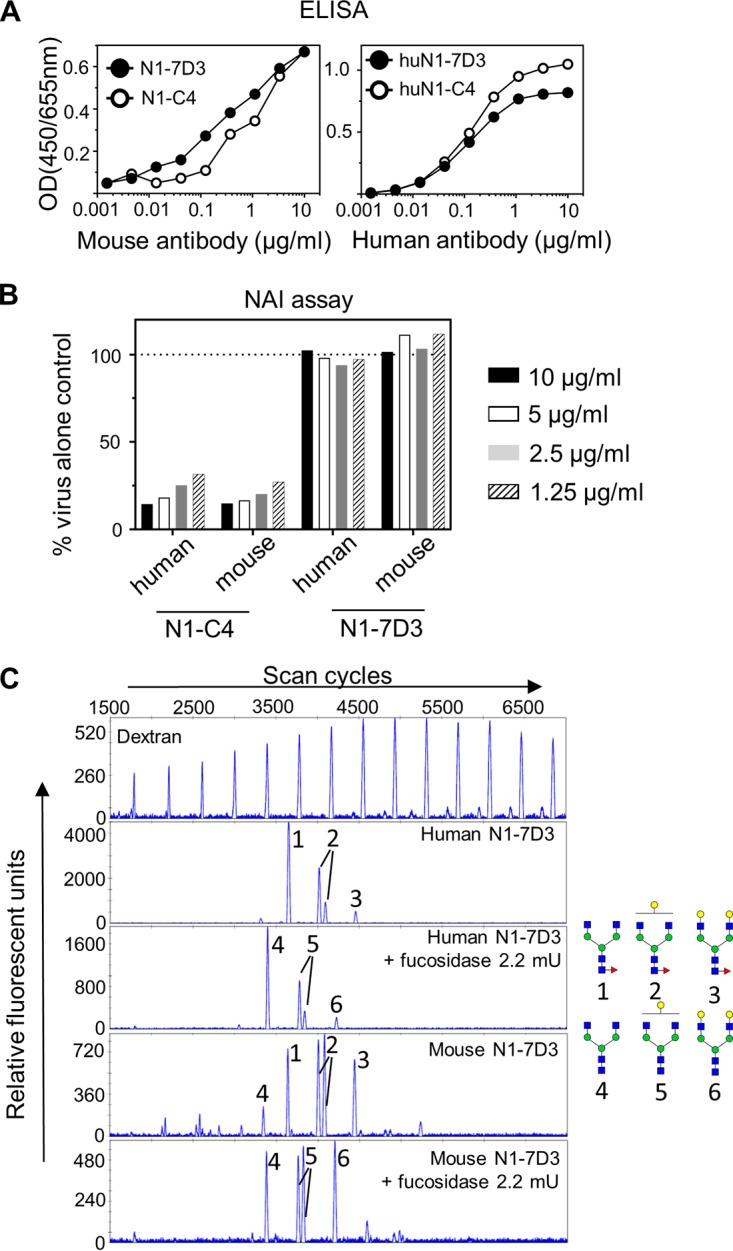
(A) HuN1-7D3 and huN1-C4 bind to recombinant NA from Bel/09. Wells of a 96-well ELISA plate were coated overnight with 0.5 μg/ml of recombinant soluble NA from Bel/09 in DPBS plus Ca2+/Mg2+. Plates were blocked with 1% BSA in PBS, and the mouse (left) or human chimera version of N1-7D3 or N1-C4 (right) was applied in increasing concentrations in 0.5% BSA in PBST. Binding was detected with either anti-mouse IgG or anti-human IgG conjugated to HRP as appropriate. OD, optical density. (B) HuN1-7D3 does not mediate NA activity against Bel/09, whereas huN1-C4 does. A constant amount of Bel/09 was incubated with 10, 5, 2.5, or 1.25 μg/ml of either huN1-C4, mouse N1-C4, huN1-7D3, or mouse N1-7D3, and NA activity was determined at 18 h postincubation on fetuin by an ELLA. Data are expressed as the percentage of the virus-alone control. NAI, NA inhibitor. (C) N-glycan profiling of mouse and humanized N1-7D3. N-glycans were isolated from mouse or humanized N1-7D3, labeled with APTS, either untreated or treated overnight with fucosidase, and analyzed by DNA sequencer-assisted fluorophore-assisted capillary electrophoresis. A labeled dextran ladder (top panel) and N-glycans from bovine RNase B (data not shown) were included as electrophoretic mobility references. The structures of the N-glycans that correspond to the indicated peaks are shown on the right. Blue squares, N-acetylglucosamine residues; green circles, mannose residues; yellow circles, galactose residues; red triangles, fucose residues.
