FIG 5.
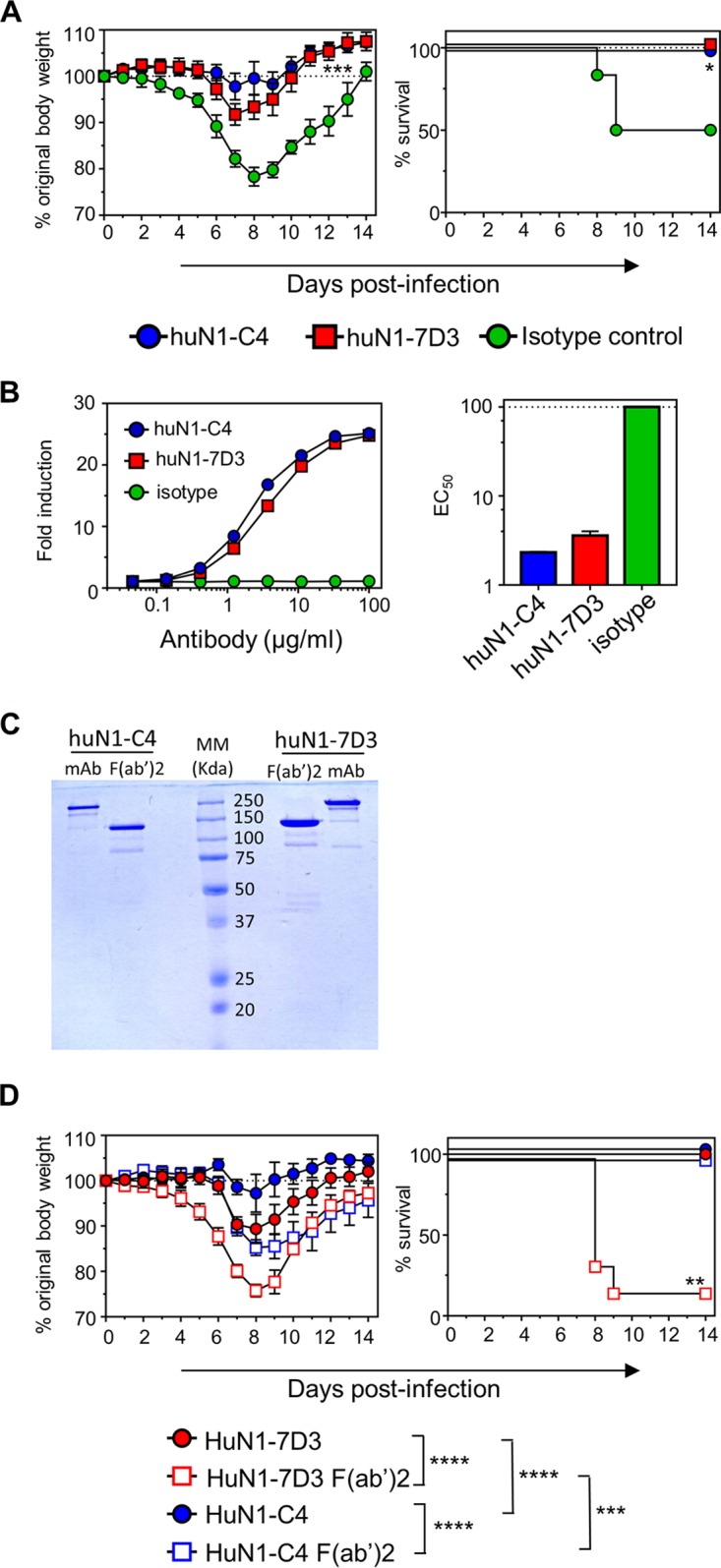
(A) HuN1-7D3 and huN1-C4 can protect against morbidity and mortality in humanized FcγR mice. Humanized FcγR mice were treated with 2.5 mg/kg μg of huN1-7D3, huN1-C4, or an isotype control via the i.n. route under isoflurane sedation. One day later, the mice were infected with 1 LD50 of Bel/09 and monitored daily over 14 days for weight loss (left panels) and survival (right panels). Weight loss data represents the mean percentage ± SEM of original body weight over time, and survival data are shown as the percentage of survival over time (n = 6 to 8). Weight loss over time was analyzed by two-way ANOVA examining the main column effects, and survival proportions were assessed using a two-tailed, log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. *, P < 0.05, and ***, P < 0.001, in comparison to isotype-treated mice. (B) Human chimeric monoclonal antibodies can engage with FcγRIIIa expressed on a Jurkat reporter cell line. Bel/09-infected MDCK cells were used as target cells for a reporter assay where huN1-C4, huN1-7D3, and an isotype control were investigated for their ability to engage the FcγRIIIa expressed on the Jurkat cell line. Antibodies were tested in triplicate in 3-fold dilutions starting from a concentration of 100 μg/ml. Fold induction was calculated from the buffer-alone control (left panel), and curves were used to define EC50 values in GraphPad Prism (right panel). (C) Coomassie-stained nonreducing SDS-PAGE confirming the correct molecular weight of F(ab′)2 fragments. HuN1-C4 and huN1-7D3 were treated with IdeS enzyme using the FragIT kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Human monoclonal antibodies and F(ab′)2 fragments were run on a 10% SDS-PAGE alongside a molecular marker (MM) to resolve proteins according to their size. The F(ab′)2 fragment preparations do not contain intact uncleaved antibody. (D) HuN1-7D3 F(ab′)2 does not protect against Bel/09 infection in humanized FcγR mice. Humanized mice were treated with equimolar amounts of monoclonal antibodies (2.5 mg/kg) or F(ab′)2 fragments (1.85 mg/kg) in a total volume of 50 μl via the intranasal route 1 day prior to infection with 2 LD50s of Bel/09. Mice were monitored for weight loss (left panel) and survival (right panel) for 14 days. Mice that had lost ≥25% of their original body weight were euthanized. Weight loss data show the mean percentage ± SEM of original body weight over time and analyzed by a two-way ANOVA examining main column effects. ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Survival data are the percentage of survival over 14 days (n = 6) and were assessed by a two-tailed, log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. **, P < 0.01 compared to all other groups. Data were pooled from two individual experiments.
