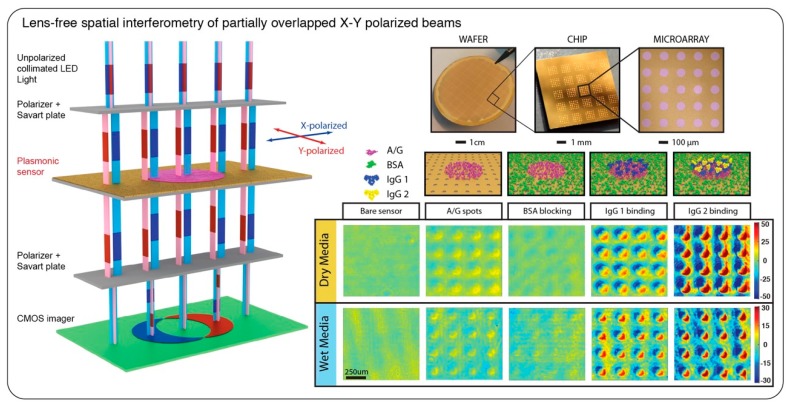
Figure 9.
(left) Large field-of view common-path spatial interferometry. In the collinear optical light-path collimated light-emitting diode (LED) light beam is first linearly polarized at 45° and then x- and y-polarized components are sheared by a savart plate (a birefringence element). This generates quasi-spatially overlapped and orthogonally polarized light beams that traverse the plasmonic microarray plate and are subsequently recombined using a second savart plate and interfered by a second polarizer. The interferogram, showing the fringes, is finally imaged by the complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensor. (right-top) Wafer-scale fabricated Au nanohole arrays cover the whole chip uniformly, allowing for high-throughput sensing. (right-bottom) Protein microarray detection on a plasmonic phase interrogation scheme. Adapted with permission from [94] Copyright 2018 Nature Publishing Group.