Scheme 2.
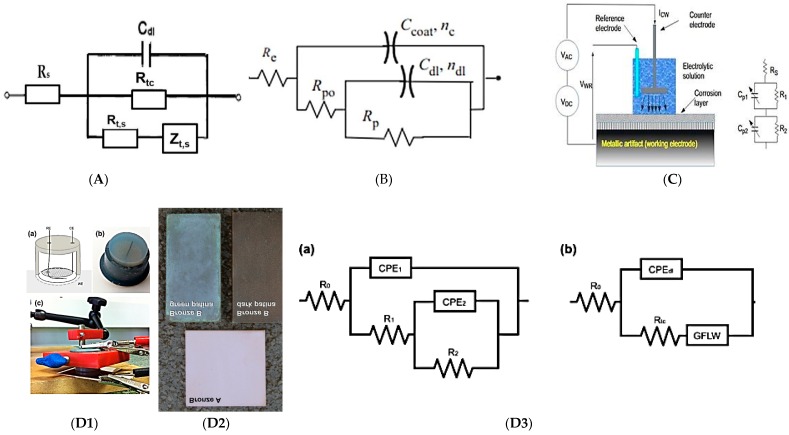
Equivalent Circuits (ECs) reported in Table 1, in particular: (A) represents the AC: Alternative Current Impedance Spectroscopy for copper in simulated tap water. (B) Represents the electrical equivalent circuit used for fitting EIS data in the presence of copper/alloy-coated patina. (C) Shows the EIS measuring principle and the corresponding EC carried out on iron/steel-coated patina. (D1) Cell design scheme (on the left); bronze coupons used for the electrochemical tests (in the middle D2) and the Equivalent electrical circuits (D3) used to analyze EIS data: (a) is the equivalent circuit with 2 nested CPE-R pairs, and (b) is the second CPE replaced by a generalized finite-length Warburg impedance.