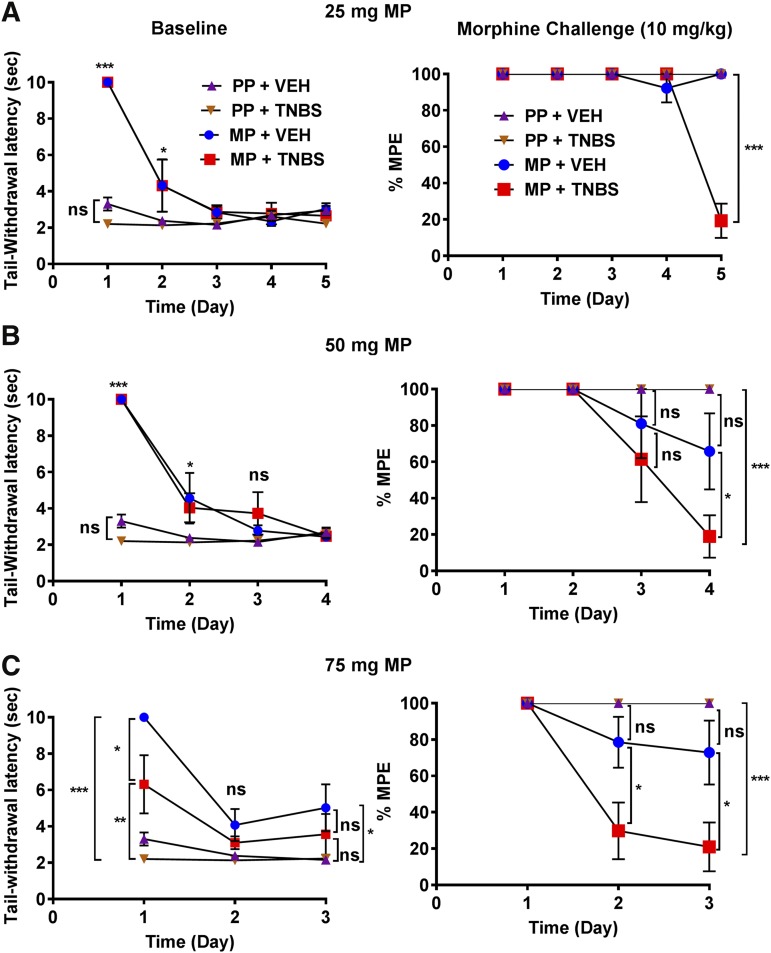
Fig. 4.
TNBS-induced colitis enhanced the rate of tolerance development in a dose- and time-dependent manner. (A–C) Daily baseline recording (left panel) shows a progressive loss of morphine response in 25-, 50-, and 75-mg MP groups over the course of 5, 4, and 3 days, respectively. Daily 10-mg/kg morphine challenge (right panel) restored the loss of morphine response in all groups except in the 25-mg MP + TNBS group on day 5, 50-mg MP + TNBS group on day 4, and 75-mg MP + TNBS group as early as day 2, indicating an enhanced development of tolerance in the inflamed mice. (A) MP + TNBS (N = 5–7/day), MP + VEH (N = 5/day), PP + TNBS (N = 5/day), PP + VEH (N = 5/day); ***P < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. (B) MP + TNBS (N = 5–8/day), MP + VEH (N = 5–7/day), PP + TNBS (N = 5/day), PP + VEH (N = 5/day); ns, not significant; *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. (C) MP + TNBS (N = 7–8/day), MP + VEH (N = 7/day), PP + TNBS (N = 5–8/day), PP + VEH (N = 5–7/day); *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis.