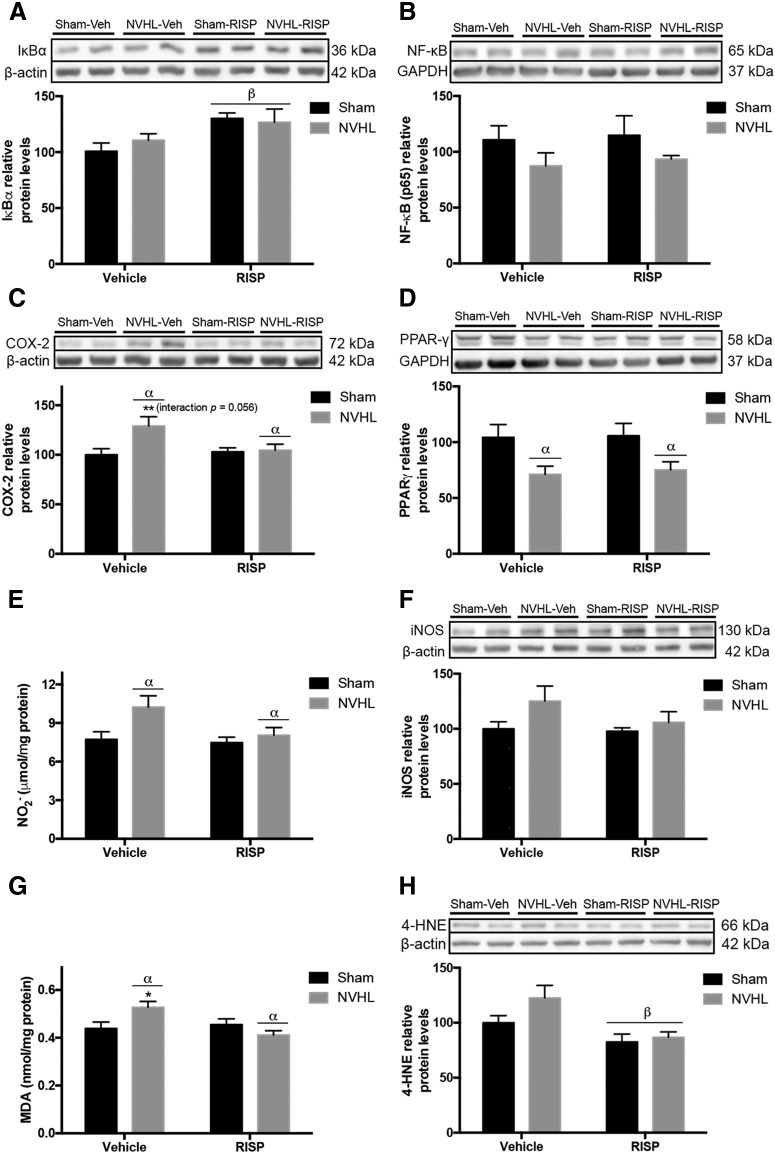
Figure 7.
NVHL generates oxidative/nitrosative stress in the PFC, that RISP treatment ameliorates. Representative Western blot images of each protein and group (n = 5/group). A, B, The NF-κB pathway was studied and (A) RISP increased IκBα levels (βRISP effect: p = 0.012) but (B) neither NVHL or RISP had an effect on NF-κB levels. C, COX-2 increased as a consequence of NVHL and because the interaction between factors was very close to the significance threshold a post hoc test was made and revealed that RISP reduced COX-2 levels in the NVHL animals (αlesion effect: p = 0.035; **p < 0.01 vs all the other groups). D, NVHL reduced PPAR-γ protein levels (αlesion effect: p = 0.004). E, NVHL increased NO2− concentration (αlesion effect: p = 0.03). F, iNOS levels remained without changes among experimental groups. G, NVHL increased MDA concentration, post hoc analyses revealed that MDA concentration decreased because of RISP in NVHL animals (αlesion effect: p = 0.012; *p < 0.05 vs all the other groups). H, RISP reduced the 4-HNE levels (βRISP effect: p = 0.004). Statistical analyses were conducted using a two-way ANOVA, Newman Keuls post hoc test.