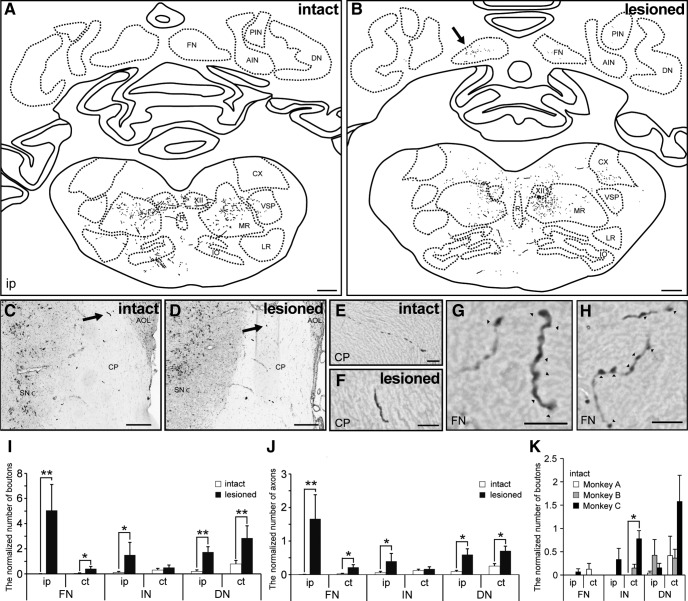
Figure 3.
Comparison of PMv projections to cerebellar nuclei between intact and lesioned monkeys. A, B, Reconstructions of a transverse section including brainstem and cerebellar nuclei of an intact (A, Monkey A) and lesioned monkey (B, Monkey D). C–F, The BDA-positive axons running through the cerebral peduncle of intact (C, E, Monkey B) and lesioned monkeys (D, F, Monkey E). The arrows in C and D indicate the BDA-positive axon in E and F, respectively. G, H, High-magnification photomicrograph showing the BDA-positive axons and boutons in the fastigial nucleus of Monkey D (B, arrow). The arrowheads indicate the BDA-positive boutons. I, J, Quantitative analysis for boutons (I) and axons (J) in the cerebellar nuclei (fastigial, interposed, and dentate) of intact and lesioned monkeys. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, according to a Mann–Whitney U test. K, Quantitative analysis of boutons in the cerebellar nuclei (fastigial, interposed, and dentate) of intact monkeys (Monkeys A–C). *p < 0.05, according to a Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's multiple-comparisons test. The number of BDA-positive boutons and axons was normalized by the number of labeled fibers at the cerebral peduncle level. Values are shown as mean ± SE. ct, Contralesional side; A/PIN, anterior/posterior interposed nucleus; DN, dentate nucleus; XII, hypoglossal nucleus; M/LR, medial/lateral reticular nucleus; CX, external cuneate nucleus; R, raphe nucleus; VSP, spinal trigeminal nucleus; IO, inferior olivary complex; CP, cerebral peduncle; SNc, pars compacta of substantia nigra; AOL, lateral terminal nucleus of accessory optic tract. Scale bars: A, B, 1 mm; C, D, 300 μm; E–H, 10 μm.