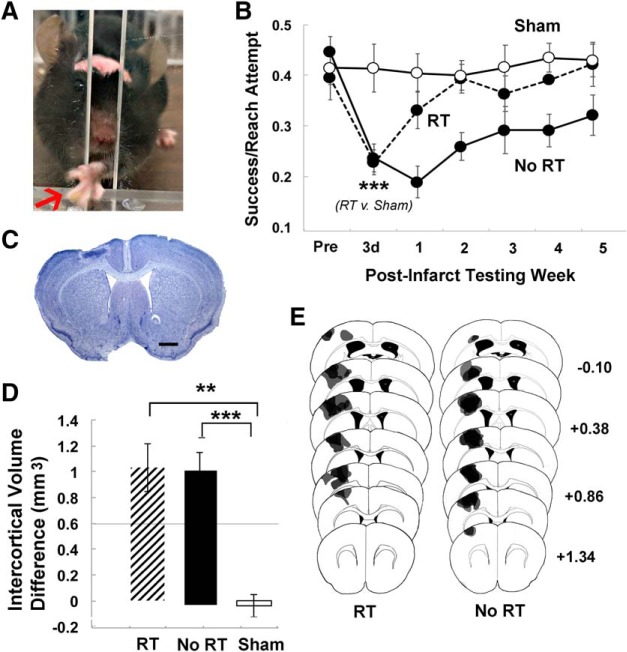
Figure 2.
RT improved postinfarct skilled reaching performance. A, Example of a mouse performing the single-seed retrieval task. The arrow points to the seed, which is grasped between digits. B, Reaching performance, measured as successful retrievals per reach attempt. Postinfarct performance significantly declined in both infarct groups. In the No RT group, performance decrements relative to Sham did not vary significantly by time over the 5 weeks after the infarct. In contrast, the RT group performed significantly worse than Sham only at postinfarct day 3 and not thereafter. C, Representative lesion in a Nissl-stained coronal section. Scale bar, 500 μm. D, Cortical lesion volume, measured as the difference in cortical volume between ipsilesional and contralesional hemispheres, was similar between the No RT and RT groups. The intercortical volume difference in both infarct groups was significantly greater than Sham. E, Representative lesion reconstructions of the infarct group overlaid on coronal section templates. Numbers to the right indicate anterior to posterior coordinates in millimeters relative to bregma. Data are mean ± SE. **p < 0.01 versus Sham. ***p < 0.0001 versus Sham.