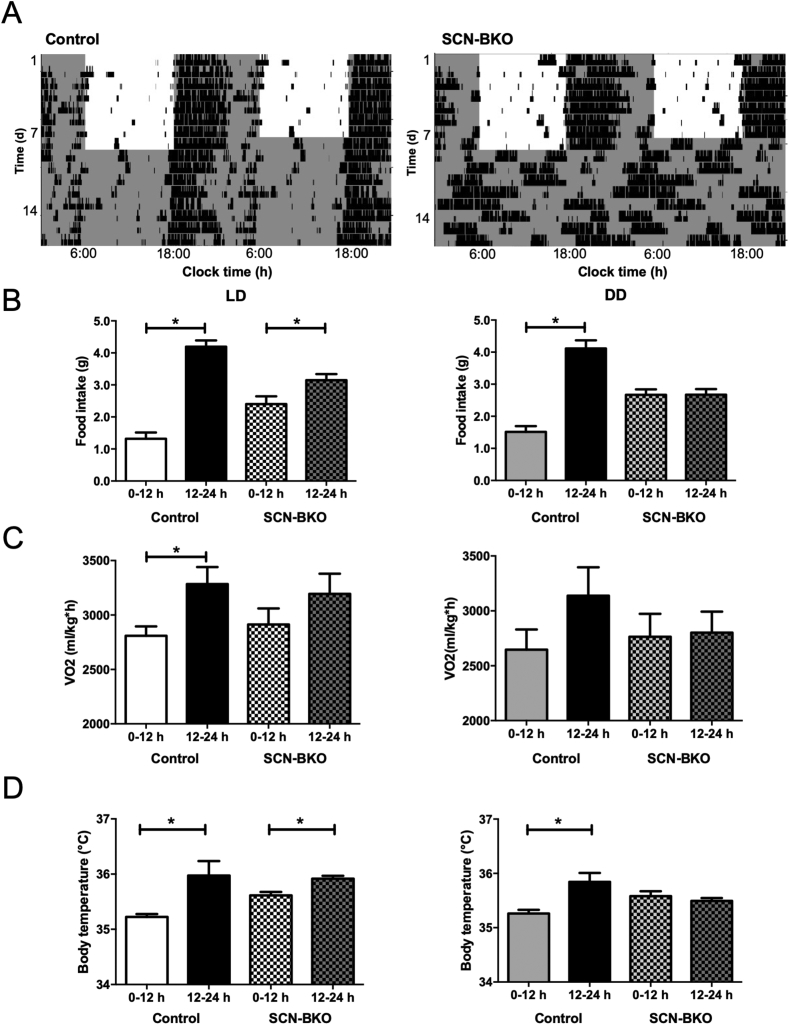
Figure 1.
SCN-BKO mice retain behavioral rhythms under light-dark but not under constant darkness conditions. A) Representative actograms of control (left) and SCN-BKO animals (right) under 12-h:12-h light-dark (LD) and constant darkness (DD) conditions. Light phases are indicated by white, dark phases by grey background. B) Day/night food intake profiles of control and SCN-BKO mice in light-dark (left; ANOVA: interaction: p < 0.001; time: p < 0.001; genotype: p = 0.933) and constant darkness (right; ANOVA: interaction: p < 0.001; time: p < 0.001; genotype: p = 0.476). C) Day/night oxygen consumption per hour normalized to body individual body weight of control and SCN-BKO mice in light-dark (left; ANOVA: interaction: p < 0.525; time: p < 0.026; genotype: p = 0.967) and constant darkness (right ANOVA: interaction: p < 0.312; time: p < 0.241; genotype: p = 0.621). D) Day/night core body temperature of control and SCN-BKO mice in light-dark (left; ANOVA: interaction: p < 0.135; time: p < 0.003; genotype: p = 0.257) and constant darkness conditions (right; ANOVA: interaction: p < 0.007; time: p < 0.033; genotype: p = 0.878). Averages ±SEM; n = 5–6 animals per condition and genotype; *: p < 0.05, 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test.