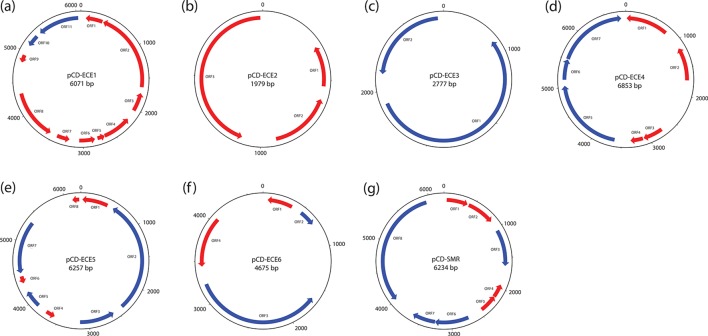
Fig. 4.
Maps of ECEs. Schematic diagram of representative members of the six putative plasmid families, pCD-ECE1 (a), pCD-ECE2 (b), pCD-ECE3 (c), pCD-ECE4 (d), pCD-ECE5 (e) and pCD-ECE6 (f), and the singleton putative multidrug-resistance plasmid pCD-SMR (g). Tick marks indicate 500 bp intervals, with every 1000 bp labelled. Red ORFs are hypothetical (no results in the automated annotation pipeline, see Methods). Blue ORFs indicate genes for which a putative function could be assigned in the automated annotation, as follows. (a) ORF10, Arc-type ribbon-helix-helix protein; ORF11, zonular occludens toxin. (b) No functions annotated. (c) ORF1, plasmid replication protein; ORF2, plasmid recombination enzyme. (d) ORF5, plasmid recombination enzyme; ORF6, penicillinase repressor; ORF7, BlaR1 peptidase M56. (e) ORF2, type III restriction enzyme (res subunit); ORF3, phage integrase family protein; ORF5, HNH endonuclease 5; ORF7, DNA-directed DNA polymerase. (f) ORF2, lambda repressor-like, DNA-binding domain superfamily protein; ORF3, alpha-helical domain, primase C-terminal like. (g) ORF3, winged-helix-like DNA-binding domain superfamily protein; ORF6, bacterial regulatory protein, TetR family; ORF7, small multidrug-resistance protein; ORF8, MobA/MobL protein.