Figure 1.
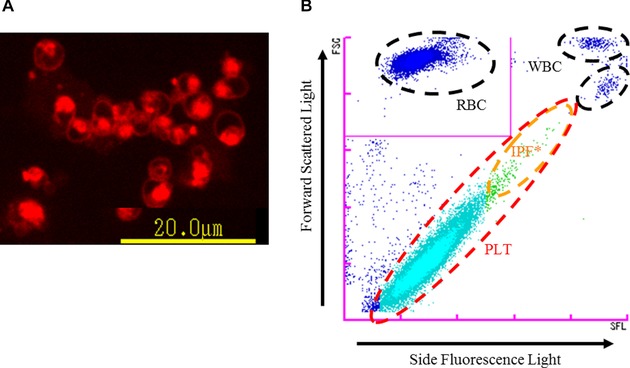
Principle of PLT‐F channel. (A) Platelets stained with the dedicated reagent of PLT‐F (fluorescent microscopy image). The staining pattern of platelets by the fluorescent dye is localized, reflecting its specific binding to nucleic acid‐rich organelles. (B) PLT‐F scattergram. After platelets are stained with fluorescence dye (A), they are differentiated using information from the forward scattered light and side fluorescence intensity (B).* IPF, immature platelet fraction.
