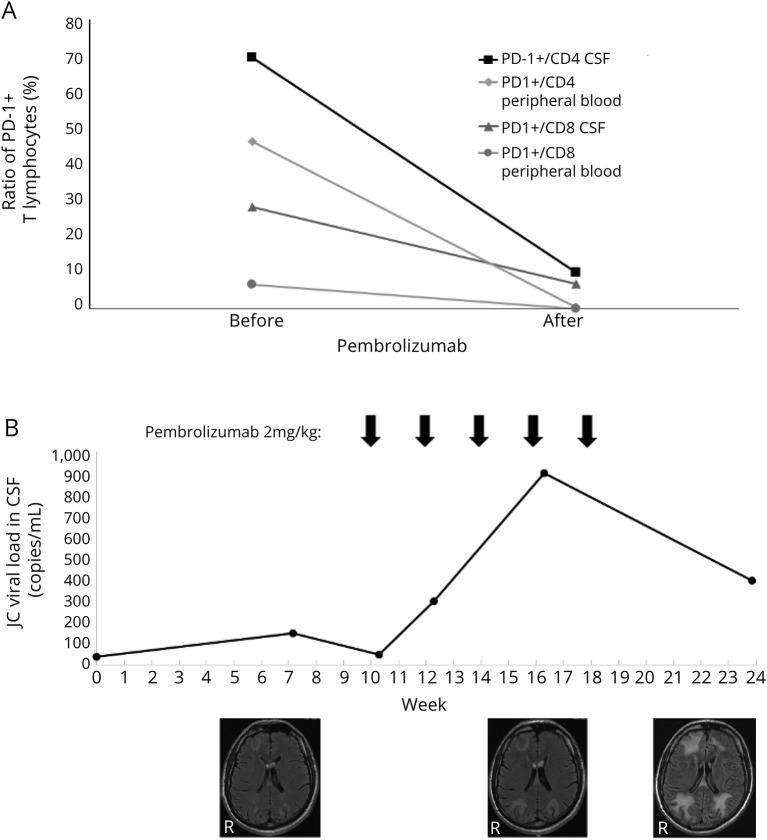
Figure. PD-1+ T lymphocytes, JC viral load, and MRI lesions in a patient with PML treated with pembrolizumab.
A 42-year-old man with primary immunodeficiency syndrome and PML was treated with pembrolizumab 2 mg/kg for 5 courses. (A) Before and after the first course of pembrolizumab, the percentage of PD-1+ cells of all CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes was analyzed by flow cytometry in CSF and peripheral blood. Pembrolizumab treatment resulted in reduced PD-1 detection on both CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes indicative of effective PD-1 blockade. (B) JC viral load in the CSF was analyzed by PCR. Structural brain damage was evaluated by FLAIR-weighted MRI. Despite the pembrolizumab treatment, the JC viral load in the CSF increased and the lesion load on MRI. A final CSF analysis after the last pembrolizumab course showed a decreasing trend of the JC viral load, but given the increasing MRI lesions and the patient's dramatic clinical deterioration at that time, further treatment did not seem appropriate anymore. FLAIR = fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; PD-1 = programmed cell death protein 1; PML = progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.