Fig. 1.
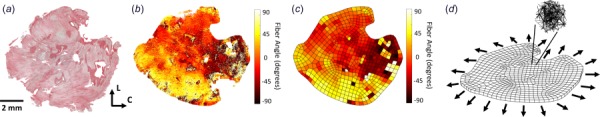
(a) Excised rat scar samples stained with picrosirius red to show collagen fiber orientations in the circumferential (C)–longitudinal (L) plane. (b) Collagen fiber orientation extracted from the tissue sample using gradient-based image processing. Each pixel was assigned an angle from –90 deg to 90 deg, representing the angle deviation from the circumferential direction (C = 0 deg, L = –90 deg or 90 deg). (c) A 2D finite element mesh was created to encompass the entire tissue area, and a nearest-neighbor linear interpolation was performed to complete the data set where fiber angle data was previously missing in (b). (d) The 2D mesh was extruded into the third dimension to create a tissue slab of uniform thickness. Aligned networks were created for each of the elements based on the fiber angle data, and each sample was subjected to uniform biaxial extension, indicated by the arrows.
