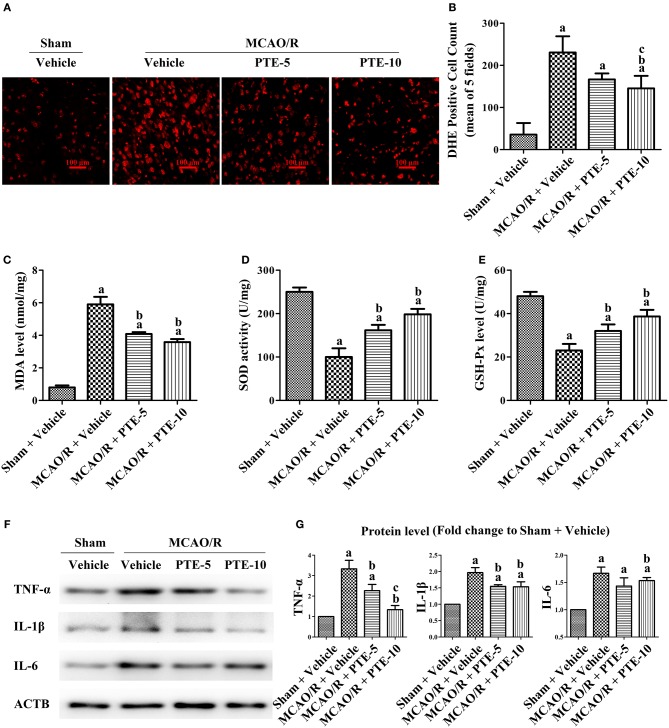
Figure 3.
Oxidative stress and inflammatory levels in MCAO/R mice with or without PTE administration. (A) The cerebral oxidative stress level in the peri-infarct area was assessed using DHE-staining (red) at 24 h after MCAO/R or sham surgery. Scale bars = 100 μm. (B) DHE-positive cells in the peri-infarct area were counted by an observer blinded to the group assignments and analyzed as the average of five random visual fields. (C–E) The levels of MDA, SOD, and GSH-Px in the infarcted hemisphere were assessed using relevant test kits at 24 h after MCAO/R or sham. (F,G) The levels of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the peri-infarct area were analyzed using western blotting at 24 h after surgery. ACTB was used as loading control, and the protein level was normalized to the Sham + Vehicle group. Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). ap < 0.05, compared with Sham + Vehicle. bp < 0.05, compared with MCAO/R + Vehicle. cp < 0.05, compared with MCAO/R + PTE-5. Significance was determined using a one-way analysis of variance. ACTB, β-actin; MCAO/R, middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion; DHE, dihydroethidium; GSH-Px, glutathione peroxidase; MDA, methane dicarboxylic aldehyde; PTE-5/10, pterostilbene 5 or 10 mg/kg; SOD, superoxide dismutase.