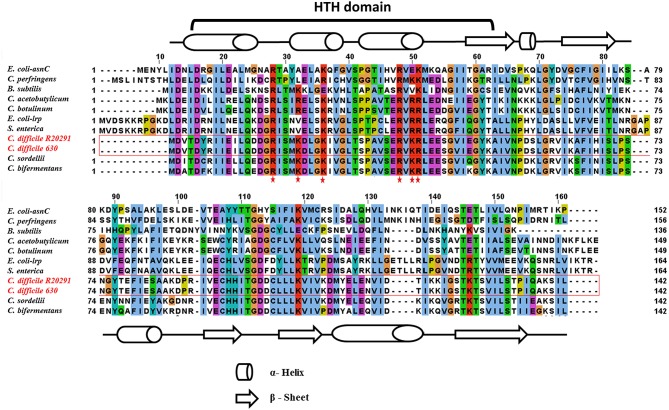
Figure 1.
Amino acid sequence alignment of C. difficile–encoded Lrp with other members of the Lrp/AsnC family. C. difficile Lrp amino acid sequences shared on average about 40% identity with the other Lrp sequences. The residues predicted to encode the DNA-binding HTH motif are identified. Secondary structural elements are indicated by barrels (α-helix) and arrows (β-sheet). Conserved lysin and arginine residues within the HTH domain are highlighted with a red star.